En las manos de Dios [in God's hands]: Religious and other forms of coping among Latinos with arthritis
- PMID: 14756618
- PMCID: PMC3657202
- DOI: 10.1037/0022-006X.72.1.91
En las manos de Dios [in God's hands]: Religious and other forms of coping among Latinos with arthritis
Abstract
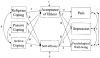
This study tested a theoretical model concerning religious, passive, and active coping; pain; and psychological adjustment among a sample of 200 Latinos with arthritis. Respondents reported using high levels of religious coping. A path analysis indicated that religious coping was correlated with active but not with passive coping. Religious coping was directly related to psychological well-being. Passive coping was associated with greater pain and worse adjustment. The effects of active coping on pain, depression, and psychological well-being were entirely indirect, mediated by acceptance of illness and self-efficacy. These findings warrant more research on the mechanisms that mediate the relationship between coping and health. This study contributes to a growing literature on religious coping among people with chronic illness, as well as contributing to a historically under-studied ethnic group.
Figures

References
-
- Abraído-Lanza AF, Guier C, Colón RM. Psychological thriving among Latinas with chronic illness. Journal of Social Issues. 1998;54:405–424.
-
- Abraído-Lanza AF, Guier C, Revenson TA. Coping and social support resources among Latinas with arthritis. Arthritis Care and Research. 1996;9:501–508. - PubMed
-
- Adler NE, Boyce T, Chesney MA, Cohen S, Folkman S, Kahn RL, Syme SL. Socioeconomic status and health. American Psychologist. 1994;49:15–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

