Cleavage furrow positioning
- PMID: 14757750
- PMCID: PMC2172245
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200310112
Cleavage furrow positioning
Abstract
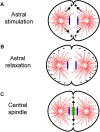
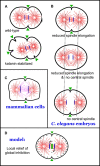
To complete the cell cycle, the cleavage furrow draws the plasma membrane toward the cell center, pinching the cytoplasm into two lobes that are subsequently separated into two cells. The position of the cleavage furrow is induced by the mitotic spindle during early anaphase. Although the mechanism of cleavage furrow positioning is not understood at a molecular level, recent results suggest that it might be mediated by local relief from the inhibitory effects of microtubules.
Copyright The Rockefeller University Press
Figures
References
-
- Adams, R.R., S.P. Wheatley, A.M. Gouldsworthy, S.E. Kandels-Lewis, M. Carmena, C. Smythe, D.L. Gerloff, and W.C. Earnshaw. 2000. INCENP binds Aurora-related kinase AIRK2 and is required to target it to the central spindle and cleavage furrow. Curr. Biol. 10:1075–1078. - PubMed

