Rap1 up-regulation and activation on plasma membrane regulates T cell adhesion
- PMID: 14757755
- PMCID: PMC2172240
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200311093
Rap1 up-regulation and activation on plasma membrane regulates T cell adhesion
Abstract
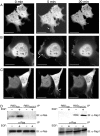
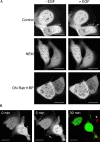
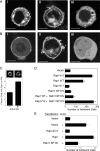
Rap1 and Ras are closely related GTPases that share some effectors but have distinct functions. We studied the subcellular localization of Rap1 and its sites of activation in living cells. Both GFP-tagged Rap1 and endogenous Rap1 were localized to the plasma membrane (PM) and endosomes. The PM association of GFP-Rap1 was dependent on GTP binding, and GFP-Rap1 was rapidly up-regulated on this compartment in response to mitogens, a process blocked by inhibitors of endosome recycling. A novel fluorescent probe for GTP-bound Rap1 revealed that this GTPase was transiently activated only on the PM of both fibroblasts and T cells. Activation on the PM was blocked by inhibitors of endosome recycling. Moreover, inhibition of endosome recycling blocked the ability of Rap1 to promote integrin-mediated adhesion of T cells. Thus, unlike Ras, the membrane localizations of Rap1 are dynamically regulated, and the PM is the principle platform from which Rap1 signaling emanates. These observations may explain some of the biological differences between these GTPases.
Copyright The Rockefeller University Press
Figures
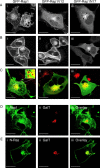
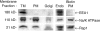
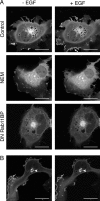
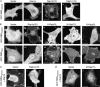
References
-
- Berger, G., R. Quarck, D. Tenza, S. Levy-Toledano, J. de Gunzburg, and E.M. Cramer. 1994. Ultrastructural localization of the small GTP-binding protein Rap1 in human platelets and megakaryocytes. Br. J. Haematol. 88:372–382. - PubMed
-
- Bos, J.L., J. de Rooij, and K.A. Reedquist. 2001. Rap1 signalling: adhering to new models. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2:369–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

