The Trypanosoma brucei spliced leader RNA and rRNA gene promoters have interchangeable TbSNAP50-binding elements
- PMID: 14757834
- PMCID: PMC373353
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh231
The Trypanosoma brucei spliced leader RNA and rRNA gene promoters have interchangeable TbSNAP50-binding elements
Abstract
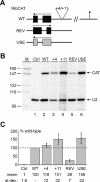
In the protist parasite Trypanosoma brucei, the small nuclear spliced leader (SL) RNA and the large rRNAs are key molecules for mRNA maturation and protein synthesis, respectively. The SL RNA gene (SLRNA) promoter recruits RNA polymerase II and consists of a bipartite upstream sequence element (USE) and an element close to the transcription initiation site. Here, we analyzed the distal part of the ribosomal (RRNA) promoter and identified two sequence blocks which, in reverse orientation, closely resemble the SLRNA USE by both sequence and spacing. A detailed mutational analysis revealed that the ribosomal (r)USE is essential for efficient RRNA transcription in vivo and that it functions in an orientation-dependent manner. Moreover, we showed that USE and rUSE are functionally interchangeable and that rUSE stably interacted with an essential factor of SLRNA transcription. Finally, we demonstrated that the T.brucei homolog of the recently characterized transcription factor p57 of the related organism Leptomonas seymouri specifically bound to USE and rUSE. Since p57 and its T.brucei counterpart are homologous to SNAP50, a component of the human small nuclear RNA gene activation protein complex (SNAPc), both SLRNA and RRNA transcription in T.brucei may depend on a SNAPc-like transcription factor.
Figures
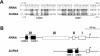

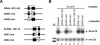



Similar articles
-
Failure to detect binding of Trypanosoma brucei SNAPc to U2 and U6 snRNA gene sequences by in vitro transcription competition and pull-down assays.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2004 Oct;137(2):293-6. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2004.06.009. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2004. PMID: 15383299
-
Trypanosome spliced leader RNA genes contain the first identified RNA polymerase II gene promoter in these organisms.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Apr 1;29(7):1556-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.7.1556. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11266558 Free PMC article.
-
Trypanosoma brucei 5'ETS A'-cleavage is directed by 3'-adjacent sequences, but not two U3 snoRNA-binding elements, which are all required for subsequent pre-small subunit rRNA processing events.J Mol Biol. 2001 Nov 2;313(4):733-49. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5078. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11697900
-
[Transcription of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes].Mol Biol (Mosk). 1994 Sep-Oct;28(5):965-77. Mol Biol (Mosk). 1994. PMID: 7990842 Review. Russian.
-
Unconventional rules of small nuclear RNA transcription and cap modification in trypanosomatids.Gene Expr. 2002;10(1-2):3-16. Gene Expr. 2002. PMID: 11868986 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TBP and SNAP50 transcription factors bind specifically to the Pr77 promoter sequence from trypanosomatid non-LTR retrotransposons.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Jun 9;14(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04803-5. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34108018 Free PMC article.
-
TbENF is an essential TbTFIIB-interacting trypanosomatid-specific factor.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2012 Feb;181(2):94-101. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2011.10.004. Epub 2011 Oct 15. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22024471 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a multisubunit transcription factor complex essential for spliced-leader RNA gene transcription in Trypanosoma brucei.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;25(16):7303-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.16.7303-7313.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16055738 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factor Analysis in Trypanosomatids.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2116:265-284. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0294-2_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32221925 Free PMC article.
-
Sm core variation in spliceosomal small nuclear ribonucleoproteins from Trypanosoma brucei.EMBO J. 2006 Oct 4;25(19):4513-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601328. Epub 2006 Sep 14. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16977313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Günzl A. (2003) Transcription. In Marr,J.J., Nielsen,T.W. and Komuniecki,R.W. (eds), Molecular Medical Parasitology. Academic Press, London, UK, pp. 47–65.
-
- Pham V.P., Qi,C.C. and Gottesdiener,K.M. (1996) A detailed mutational analysis of the VSG gene expression site promoter. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol., 75, 241–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions

