Probiotics inhibit TNF-alpha-induced interleukin-8 secretion of HT29 cells
- PMID: 14760780
- PMCID: PMC4724907
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i3.455
Probiotics inhibit TNF-alpha-induced interleukin-8 secretion of HT29 cells
Abstract
Aim: To study the effect of probiotics on interleukin-8 secretion in intestinal epithelia when stimulated by proinflammatory cytokines.
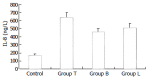
Methods: Colonic adenocarcinoma HT29 cells were cultured and divided into four groups: control, TNF-alpha (group T in short), bifidobacterium (group B), lactobacillus (group L). B. Longum and L. bulgaricus were suspended in culture medium with a concentration of 1 x 10(8) cfu/ml and added into 24 wells respectively. One hour later TNF-alpha (10 ng/ml) was added into each well of groups T, B, L. The supernatants were collected and measured for IL-8 after 3 hours, nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) p65 was also examined by Western blotting.
Results: There was less interleukin-8 secretion in HT29 cells when preincubated with B. Longum or L. bulgaricus compared with group T. Less p65 appeared in nuclei in groups B and L compared with group T, as detected by Western blot.
Conclusion: Probiotics can suppress interleukin-8 secretion in intestinal epithelia when stimulated by proinflammatory cytokines, which is most likely mediated by NF-kappaB.
Figures

References
-
- Gordon JI, Hooper LV, McNevin MS, Wong M, Bry L. Epithelial cell growth and differentiation. III. Promoting diversity in the intestine: conversations between the microflora, epithelium, and diffuse GALT. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:G565–G570. - PubMed
-
- Campbell N, Yio XY, So LP, Li Y, Mayer L. The intestinal epithelial cell: processing and presentation of antigen to the mucosal immune system. Immunol Rev. 1999;172:315–324. - PubMed
-
- Hausmann M, Kiessling S, Mestermann S, Webb G, Spöttl T, Andus T, Schölmerich J, Herfarth H, Ray K, Falk W, et al. Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 are up-regulated during intestinal inflammation. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1987–2000. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

