Identification of genes controlled by the essential YycG/YycF two-component system of Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 14762013
- PMCID: PMC344212
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.4.1175-1181.2004
Identification of genes controlled by the essential YycG/YycF two-component system of Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
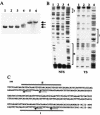
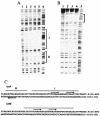
The YycG/YycF essential two-component system (TCS), originally identified in Bacillus subtilis, is very highly conserved and appears to be specific to low-G+C gram-positive bacteria, including several pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus. By studying growth of S. aureus cells where the yyc operon is controlled by an isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG)-inducible promoter, we have shown that this system is essential in S. aureus during growth at 37 degrees C and that starvation for the YycG/YycF regulatory system leads to cell death. During a previous study of the YycG/YycF TCS of B. subtilis, we defined a potential YycF consensus recognition sequence, consisting of two hexanucleotide direct repeats, separated by five nucleotides [5'-TGT(A/T)A(A/T/C)-N(5)-TGT(A/T)A(A/T/C)-3']. A detailed DNA motif analysis of the S. aureus genome indicates that there are potentially 12 genes preceded by this sequence, 5 of which are involved in virulence. An in vitro approach was undertaken to determine which of these genes are controlled by YycF. The YycG and YycF proteins of S. aureus were overproduced in Escherichia coli and purified. Autophosphorylation of the YycG kinase and phosphotransfer to YycF were shown in vitro. Gel mobility shift and DNase I footprinting assays were used to show direct binding in vitro of purified YycF to the promoter region of the ssaA gene, encoding a major antigen and previously suggested to be controlled by YycF. YycF was also shown to bind specifically to the promoter regions of two genes, encoding the IsaA antigen and the LytM peptidoglycan hydrolase, in agreement with the proposed role of this system in controlling virulence and cell wall metabolism.
Figures


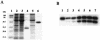
Similar articles
-
Genes controlled by the essential YycG/YycF two-component system of Bacillus subtilis revealed through a novel hybrid regulator approach.Mol Microbiol. 2003 Sep;49(6):1639-55. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03661.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12950927
-
The essential two-component regulatory system encoded by yycF and yycG modulates expression of the ftsAZ operon in Bacillus subtilis.Microbiology (Reading). 2000 Jul;146 ( Pt 7):1573-1583. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-7-1573. Microbiology (Reading). 2000. PMID: 10878122
-
Tearing down the wall: peptidoglycan metabolism and the WalK/WalR (YycG/YycF) essential two-component system.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:214-28. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792692 Review.
-
Molecular characterization of the essential response regulator protein YycF in Bacillus subtilis.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003;6(3-4):155-63. doi: 10.1159/000077246. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 15153768
-
A matter of life and death: cell wall homeostasis and the WalKR (YycGF) essential signal transduction pathway.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Dec;70(6):1307-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06483.x. Epub 2008 Oct 23. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 19019149 Review.
Cited by
-
YsxC, an essential protein in Staphylococcus aureus crucial for ribosome assembly/stability.BMC Microbiol. 2009 Dec 18;9:266. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-266. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 20021644 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of peptidoglycan hydrolases: localization, abundance, and activity.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2023 Apr;72:102279. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2023.102279. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36812681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcus aureus Extracellular Vesicles Elicit an Immunostimulatory Response in vivo on the Murine Mammary Gland.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Aug 22;8:277. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00277. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30186772 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction of the Vancomycin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Phenotype From a Vancomycin-Intermediate S. aureus XN108.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 28;9:2955. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02955. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30546356 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Histidine Kinase-Targeted Antimicrobial Agents.Front Chem. 2022 Jul 4;10:866392. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.866392. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35860627 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amrein, K. E., B. Takacs, M. Stieger, J. Molnos, N. A. Flint, and P. Burn. 1995. Purification and characterization of recombinant human p50csk protein-tyrosine kinase from an Escherichia coli expression system overproducing the bacterial chaperones GroES and GroEL. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:1048-1052. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang, S., D. M. Sievert, J. C. Hageman, M. L. Boulton, F. C. Tenover, F. P. Downes, S. Shah, J. T. Rudrik, G. R. Pupp, W. J. Brown, D. Cardo, and S. K. Fridkin. 2003. Infection with vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus containing the vanA resistance gene. N. Engl. J. Med. 348:1342-1347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

