Ephrin-A5 exerts positive or inhibitory effects on distinct subsets of EphA4-positive motor neurons
- PMID: 14762125
- PMCID: PMC6793576
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4719-03.2004
Ephrin-A5 exerts positive or inhibitory effects on distinct subsets of EphA4-positive motor neurons
Abstract
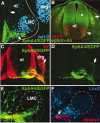
Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and ephrins are required for axon patterning and plasticity in the developing nervous system. Typically, Eph-ephrin interactions promote inhibitory events; for example, prohibiting the entry of neural cells into certain embryonic territories. Here, we show that distinct subsets of motor neurons that express EphA4 respond differently to ephrin-A5. EphA4-positive LMC(l) axons avoid entering ephrin-A5-positive hindlimb mesoderm. In contrast, EphA4-positive MMC(m) axons extend through ephrin-A5-positive rostral half-sclerotome. Blocking EphA4 activation in MMC(m) neurons or expanding the domain of ephrin-A5 expression in the somite results in the aberrant growth of MMC(m) axons into the caudal half-sclerotome. Moreover, premature expression of EphA4 in MMC(m) neurons leads to a portion of their axons growing into novel ephrin-A5-positive territories. Together, these results indicate that EphA4-ephrin-A5 signaling acts in a positive manner to constrain MMC(m) axons to the rostral half-sclerotome. Furthermore, we show that Eph activation localizes to distinct subcellular compartments of LMC(l) and MMC(m) neurons, consistent with distinct EphA4 signaling cascades in these neuronal subpopulations.
Figures







References
-
- Brittis PA, Qiang L, Flanagan JG (2002) Axonal protein synthesis provides a mechanism for localized regulation at an intermediate target. Cell 110: 223–235. - PubMed
-
- Campbell DS, Holt CE (2001) Chemotropic responses of retinal growth cones mediated by rapid local protein synthesis and degradation. Neuron 32: 1013–1026. - PubMed
-
- Dickson BJ (2002) Molecular mechanisms of axon guidance. Science 298: 1959–1964. - PubMed
-
- Eberhart J, Swartz M, Koblar SA, Pasquale EB, Tanaka H, Krull CE (2000) Expression of EphA4, ephrin-A2 and ephrin-A5 during axon outgrowth to the hindlimb indicates potential roles in pathfinding. Dev Neurosci 22: 237–250. - PubMed
-
- Eberhart J, Swartz ME, Koblar SA, Pasquale EB, Krull CE (2002) EphA4 constitutes a population-specific guidance cue for motor neurons. Dev Biol 247: 89–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
