IL-15 enhances the in vivo antitumor activity of tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 14762166
- PMCID: PMC357036
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307298101
IL-15 enhances the in vivo antitumor activity of tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells
Abstract
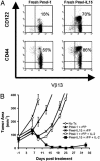
IL-15 and IL-2 possess similar properties, including the ability to induce T cell proliferation. However, whereas IL-2 can promote apoptosis and limit CD8(+) memory T cell survival and proliferation, IL-15 helps maintain a memory CD8(+) T cell population and can inhibit apoptosis. We sought to determine whether IL-15 could enhance the in vivo function of tumor/self-reactive CD8(+) T cells by using a T cell receptor transgenic mouse (pmel-1) whose CD8(+) T cells recognize an epitope derived from the self/melanoma antigen gp100. By removing endogenous IL-15 by using tumor-bearing IL-15 knockout hosts or supplementing IL-15 by means of exogenous administration, as a component of culture media or as a transgene expressed by adoptively transferred T cells, we demonstrate that IL-15 can improve the in vivo antitumor activity of adoptively transferred CD8(+) T cells. These results provide several avenues for improving adoptive immunotherapy of cancer in patients.
Figures
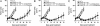


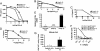

References
-
- Rosenberg, S. A. (2001) Nature 411, 380–384. - PubMed
-
- Van Parijs, L., Refaeli, Y., Lord, J. D., Nelson, B. H., Abbas, A. K. & Baltimore, D. (1999) Immunity 11, 281–288. - PubMed
-
- Refaeli, Y., Van Parijs, L., London, C. A., Tschopp, J. & Abbas, A. K. (1998) Immunity 8, 615–623. - PubMed
-
- Ku, C. C., Murakami, M., Sakamoto, A., Kappler, J. & Marrack, P. (2000) Science 288, 675–678. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

