Small potassium ion channel proteins encoded by chlorella viruses
- PMID: 14762169
- PMCID: PMC397378
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307824100
Small potassium ion channel proteins encoded by chlorella viruses
Abstract
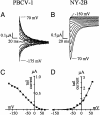
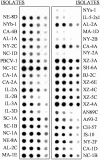
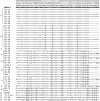
Kcv, a 94-aa protein encoded by Paramecium bursaria chlorella virus 1, is the smallest known protein to form a functional potassium ion channel and basically corresponds to the "pore module" of potassium channels. Both viral replication and channel activity are inhibited by the ion channel blockers barium and amantadine but not by cesium. Genes encoding Kcv-like proteins were isolated from 40 additional chlorella viruses. Differences in 16 of the 94 amino acids were detected, producing six Kcv-like proteins with amino acid substitutions occurring in most of the functional domains of the protein (N terminus, transmembrane 1, pore helix, selectivity filter, and transmembrane 2). The six proteins form functional potassium selective channels in Xenopus oocytes with different properties including altered current kinetics and inhibition by cesium. The amino acid changes together with the different properties observed in the six Kcv-like channels will be used to guide site-directed mutations, either singularly or in combination, to identify key amino acids that confer specific properties to Kcv.
Figures



References
-
- Van Etten, J. L. & Meints, R. H. (1999) Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 53, 447–494. - PubMed
-
- Van Etten, J. L. (2003) Annu. Rev. Genet. 37, 153–195. - PubMed
-
- Plugge, B., Gazzarrini, S., Nelson, M., Cerana, R., Van Etten, J. L., Derst, C., DiFrancesco, D., Moroni, A. & Thiel, G. (2000) Science 287, 1641–1644. - PubMed
-
- Moroni, A., Viscomi, C., Sangiorgio, V., Pagliuca, C., Meckel, T., Horvath, F., Gazzarrini, S., Valbuzzi, P., Van Etten, J. L., DiFrancesco, D. & Thiel, G. (2002) FEBS Lett. 530, 65–69. - PubMed
-
- Gazzarrini, S., Severino, M., Lombardi, M., Morandi, M., DiFrancesco, D., Van Etten, J., Thiel, G. & Moroni, A. (2003) FEBS Lett. 552, 12–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

