Coordinated regulation of genes for secretion in tobacco at late developmental stages: association with resistance against oomycetes
- PMID: 14764907
- PMCID: PMC344560
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.034173
Coordinated regulation of genes for secretion in tobacco at late developmental stages: association with resistance against oomycetes
Abstract
Besides the systemic acquired resistance (SAR) induced in response to microbial stimulation, host plants may also acquire resistance to pathogens in response to endogenous stimuli associated with their own development. In tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum), the vegetative-to-flowering transition comes along with a susceptibility-to-resistance transition to the causal agent of black shank disease, the oomycete Phytophthora parasitica. This resistance affects infection effectiveness and hyphal expansion and is associated with extracellular accumulation of a cytotoxic activity that provokes in vitro cell death of P. parasitica zoospores. As a strategy to determine the extracellular events important for restriction of pathogen growth, we screened the tobacco genome for genes encoding secreted or membrane-bound proteins expressed in leaves of flowering plants. Using a signal sequence trap approach in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), 298 clones were selected that appear to encode for apoplastic, cell wall, or membrane-bound proteins involved in stress response, in plant defense, or in cell wall modifications. Microarray and northern-blot analyses revealed that, at late developmental stages, leaves were characterized by the coordinate up-regulation of genes involved in SAR and in peroxidative cross-linking of structural proteins to cell wall. This suggests the potential involvement of these genes in extracellular events that govern the expression of developmental resistance. The analysis of the influence of salicylic acid on mRNA accumulation also indicates a more complex network for regulation of gene expression at a later stage of tobacco development than during SAR. Further characterization of these genes will permit the formulation of hypotheses to explain resistance and to establish the connection with development.
Figures
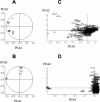
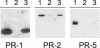
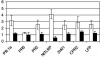
References
-
- Abad A, Cardin L, Poupet A, Ponchet M (1989) Comparison of pathogenesis related “b1” protein determination obtained by Elisa and HPLC techniques. J Phytopathol 124: 175–188
-
- Abad LR, D'Urzo MP, Liu D, Narasimhan ML, Reuveni M, Zhu J, Niu X, Singh NK, Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA (1996) Antifungal activity of tobacco osmotin has specificity and involves plasma membrane permeabilization. Plant Sci 118: 11–23
-
- Abedon BG, Tracy WF (1996) Congrass1 of maize (Zea mays L.) delays development of adult plant resistance to common rust (Puccinia sorgi Schw) and European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis Hubner). J Hered 87: 219–223
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

