The Yersinia adhesin YadA collagen-binding domain structure is a novel left-handed parallel beta-roll
- PMID: 14765110
- PMCID: PMC381008
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600100
The Yersinia adhesin YadA collagen-binding domain structure is a novel left-handed parallel beta-roll
Abstract
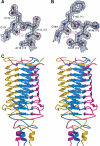
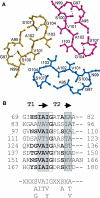
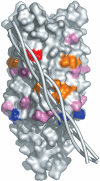
The crystal structure of the recombinant collagen-binding domain of Yersinia adhesin YadA from Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3 was solved at 1.55 A resolution. The trimeric structure is composed of head and neck regions, and the collagen binding head region is a novel nine-coiled left-handed parallel beta-roll. Before the beta-roll, the polypeptide loops from one monomer to the rest, and after the beta-roll the neck region does the same, making the transition from the globular head region to the narrower stalk domain. This creates an intrinsically stable 'lock nut' structure. The trimeric form of YadA is required for collagen binding, and mutagenesis of its surface residues allowed identification of a putative collagen-binding surface. Furthermore, a new structure-sequence motif for YadA beta-roll was used to identify putative YadA-head-like domains in a variety of human and plant pathogens. Such domains may therefore be a common bacterial strategy for avoiding host response.
Figures
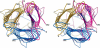
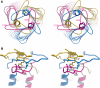
References
-
- Aghajari N, Van Petegem F, Villeret V, Chessa J-P, Gerday C, Haser R, Van Beeumen J (2003) Crystal structures of a psychrophilic metalloprotease reveal new insights into catalysis by cold-adapted psroteases. PROTEINS: Struct Funct Genet 50: 636–647 - PubMed
-
- Baumann U (1994) Crystal structure of the 50 kDa metallo protease from Serratia marcescens. J Mol Biol 242: 244–251 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

