Crystal structure of a myristoylated CAP-23/NAP-22 N-terminal domain complexed with Ca2+/calmodulin
- PMID: 14765114
- PMCID: PMC381001
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600093
Crystal structure of a myristoylated CAP-23/NAP-22 N-terminal domain complexed with Ca2+/calmodulin
Abstract
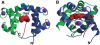
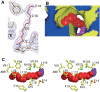
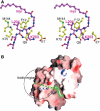
A variety of viral and signal transduction proteins are known to be myristoylated. Although the role of myristoylation in protein-lipid interaction is well established, the involvement of myristoylation in protein-protein interactions is less well understood. CAP-23/NAP-22 is a brain-specific protein kinase C substrate protein that is involved in axon regeneration. Although the protein lacks any canonical calmodulin (CaM)-binding domain, it binds CaM with high affinity. The binding of CAP-23/NAP-22 to CaM is myristoylation dependent and the N-terminal myristoyl group is directly involved in the protein-protein interaction. Here we show the crystal structure of Ca2+-CaM bound to a myristoylated peptide corresponding to the N-terminal domain of CAP-23/NAP-22. The myristoyl moiety of the peptide goes through a hydrophobic tunnel created by the hydrophobic pockets in the N- and C-terminal domains of CaM. In addition to the myristoyl group, several amino-acid residues in the peptide are important for CaM binding. This is a novel mode of binding and is very different from the mechanism of binding in other CaM-target complexes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The binding of myristoylated N-terminal nonapeptide from neuro-specific protein CAP-23/NAP-22 to calmodulin does not induce the globular structure observed for the calmodulin-nonmyristylated peptide complex.Protein Sci. 2000 Oct;9(10):1905-13. doi: 10.1110/ps.9.10.1905. Protein Sci. 2000. PMID: 11106163 Free PMC article.
-
Myristoylation-regulated direct interaction between calcium-bound calmodulin and N-terminal region of pp60v-src.J Mol Biol. 2004 Apr 16;338(1):169-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.02.041. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15050832
-
Identification of the calmodulin-binding domain of neuron-specific protein kinase C substrate protein CAP-22/NAP-22. Direct involvement of protein myristoylation in calmodulin-target protein interaction.J Biol Chem. 1999 Apr 23;274(17):11848-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.17.11848. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10207003
-
A Non-Canonical Calmodulin Target Motif Comprising a Polybasic Region and Lipidated Terminal Residue Regulates Localization.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 15;21(8):2751. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082751. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of calmodulin's functional versatility.Biochem Cell Biol. 1998;76(2-3):313-23. doi: 10.1139/bcb-76-2-3-313. Biochem Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9923700 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure guided modification of 2-chloro-5-(ethyl-phenyl-sulfamoyl)-N-[2-(2-oxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-phenyl]-benzamide to afford selective inhibitors of Cryptosporidium parvum N-myristoyltransferase.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2025 Apr 15;119:130092. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2025.130092. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2025. PMID: 39778753
-
Identification of potent and selective N-myristoyltransferase inhibitors of Plasmodium vivax liver stage hypnozoites and schizonts.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 5;14(1):5408. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41119-7. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37669940 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of K-Ras4B Membrane Binding by Calmodulin.Biophys J. 2016 Jul 12;111(1):113-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.05.042. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27410739 Free PMC article.
-
PCaPs, possible regulators of PtdInsP signals on plasma membrane.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Jul;5(7):848-50. doi: 10.4161/psb.5.7.11825. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20448467 Free PMC article.
-
A high-affinity cocaine binding site associated with the brain acid soluble protein 1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Apr 19;119(16):e2200545119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2200545119. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35412917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ames JB, Ishima R, Tanaka T, Gordon JI, Stryer L, Ikura M (1997) Molecular mechanics of calcium-myristoyl switches. Nature 389: 198–202 - PubMed
-
- Bomze HM, Bulsara KR, Iskandar BJ, Caroni P, Skene JHP (2001) Spinal axon regeneration evoked by replacing two growth cone proteins in adult neurons. Nat Neurosci 4: 38–43 - PubMed
-
- Brunger A, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Rice LM, Simonson T, Warren GL (1998) Crystallography and NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D 54: 905–921 - PubMed
-
- CCP4 (1994) The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D 50: 760–763 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

