DCX, a new mediator of the JNK pathway
- PMID: 14765123
- PMCID: PMC380994
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600079
DCX, a new mediator of the JNK pathway
Abstract
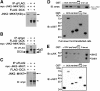
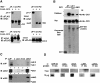
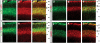
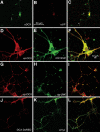
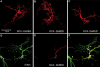
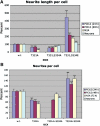
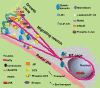
Mutations in the X-linked gene DCX result in lissencephaly in males, and abnormal neuronal positioning in females, suggesting a role for this gene product during neuronal migration. In spite of several known protein interactions, the involvement of DCX in a signaling pathway is still elusive. Here we demonstrate that DCX is a substrate of JNK and interacts with both c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and JNK interacting protein (JIP). The localization of this signaling module in the developing brain suggests its functionality in migrating neurons. The localization of DCX at neurite tips is determined by its interaction with JIP and by the interaction of the latter with kinesin. DCX is phosphorylated by JNK in growth cones. DCX mutated in sites phosphorylated by JNK affected neurite outgrowth, and the velocity and relative pause time of migrating neurons. We hypothesize that during neuronal migration, there is a need to regulate molecular motors that are working in the cell in opposite directions: kinesin (a plus-end directed molecular motor) versus dynein (a minus-end directed molecular motor).
Figures


References
-
- Aicardi J (1989) The lissencephaly syndromes. Int Pediat 4: 118–126
-
- Assadi AH, Zhang G, Beffert U, McNeil RS, Renfro AL, Niu S, Quattrocchi CC, Antalffy BA, Sheldon M, Armstrong DD, Wynshaw-Boris A, Herz J, D'Arcangelo G, Clark GD (2003) Interaction of reelin signaling and Lis1 in brain development. Nat Genet 35: 270–276 - PubMed
-
- Barth PG (1987) Disorders of neuronal migration. Can J Neurol Sci 14: 1–16 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

