Use of TaqMan 5' nuclease real-time PCR for quantitative detection of Mycoplasma genitalium DNA in males with and without urethritis who were attendees at a sexually transmitted disease clinic
- PMID: 14766837
- PMCID: PMC344445
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.2.683-692.2004
Use of TaqMan 5' nuclease real-time PCR for quantitative detection of Mycoplasma genitalium DNA in males with and without urethritis who were attendees at a sexually transmitted disease clinic
Abstract
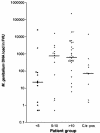
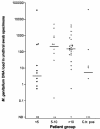
Mycoplasma genitalium is a cause of nongonococcal urethritis, particularly in patients not infected with Chlamydia trachomatis. A quantitative 5' nuclease assay (TaqMan PCR) was developed and validated. The assay detected a fragment of the MgPa adhesin gene by use of a TaqMan MGB (minor groove binder) probe and included an internal processing control to detect PCR inhibition. Urethral swab specimens and first-void urine samples from M. genitalium-positive men were examined, and the M. genitalium DNA load was correlated to symptoms and signs. The assay consistently detected <5 genome copies without cross-reactions with other mycoplasmas. Urine and urethral swab specimens from men with urethritis had higher M. genitalium DNA loads than specimens from men without urethritis. However, a very broad overlap of DNA loads between patients with and without urethritis was observed. Urethral swab specimens from patients with urethral discharge had a significantly higher DNA load than specimens from patients without discharge. This correlation was not found in first-void urine specimens.
Figures


References
-
- Björnelius, E., P. Lidbrink, and J. S. Jensen. 2000. Mycoplasma genitalium in non-gonococcal urethritis—a study in Swedish male STD patients. Int. J. STD AIDS 11:292-296. - PubMed
-
- Horner, P., B. Thomas, C. Gilroy, M. Egger, M. McClure, and D. Taylor-Robinson. 2003. Antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis heat-shock protein 60 kDa and detection of Mycoplasma genitalium and Ureaplasma urealyticum are associated independently with chronic nongonococcal urethritis. Sex. Transm. Dis. 30:129-133. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

