p38 MAPK-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activity is required for skeletal muscle differentiation: role of interleukin-6
- PMID: 14767066
- PMCID: PMC379295
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-08-0585
p38 MAPK-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activity is required for skeletal muscle differentiation: role of interleukin-6
Abstract
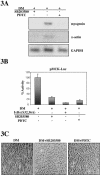
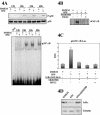
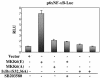
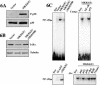
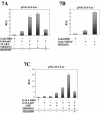
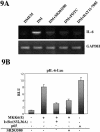
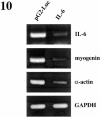
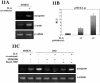
p38 MAPK and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling pathways have been implicated in the control of skeletal myogenesis. However, although p38 is recognized as a potent activator of myoblast differentiation, the role of NF-kappaB remains controversial. Here, we show that p38 is activated only in differentiating myocytes, whereas NF-kappaB activity is present both in proliferation and differentiation stages. NF-kappaB activation was found to be dependent on p38 activity during differentiation, being NF-kappaB an effector of p38, thus providing a novel mechanism for the promyogenic effect of p38. Activation of p38 in C2C12 cells induced the activity of NF-kappaB, in a dual way: first, by reducing IkappaBalpha levels and inducing NF-kappaB-DNA binding activity and, second, by potentiating the transactivating activity of p65-NF-kappaB. Finally, we show that interleukin (IL)-6 expression is induced in C2C12 differentiating myoblasts, in a p38- and NF-kappaB-dependent manner. Interference of IL-6 mRNA reduced, whereas its overexpression increased, the extent of myogenic differentiation; moreover, addition of IL-6 was able to rescue significantly the negative effect of NF-kappaB inhibition on this process. This study provides the first evidence of a crosstalk between p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways during myogenesis, with IL-6 being one of the effectors of this promyogenic mechanism.
Figures



References
-
- Baeuerle, P.A., and Baltimore, D. (1996). NF-kB: ten years after. Cell 87, 13-20. - PubMed
-
- Bird, T.A., Schooley, K., Dower, S.K., Hagen, H., and Virca, G.D. (1997). Activation of nuclear transcription factor NF-kappaB by interleukin-1 is accompanied by casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of the p65 subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 32606-32612. - PubMed
-
- Black, B.L., and Olson, E.N. (1998). Transcriptional control of muscle development by myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2) proteins. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 14, 167-196. - PubMed
-
- Canicio, J., Ruiz-Lozano, P., Carrasco, M., Palacin, M., Chien, K., Zorzano, A., and Kaliman, P. (2001). Nuclear factor kappa B-inducing kinase and Ikappa B kinase-alpha signal skeletal muscle cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 20228-20233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

