SARS-associated viral hepatitis caused by a novel coronavirus: report of three cases
- PMID: 14767982
- PMCID: PMC7165792
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.20111
SARS-associated viral hepatitis caused by a novel coronavirus: report of three cases
Abstract
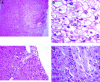
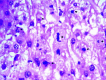
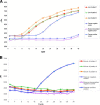
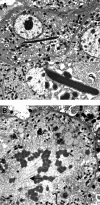
Liver impairment is commonly reported in up to 60% of patients who suffer from severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Here we report the clinical course and liver pathology in three SARS patients with liver impairment. Three patients who fulfilled the World Health Organization case definition of probable SARS and developed marked elevation of alanine aminotransferase were included. Percutaneous liver biopsies were performed. Liver specimens were examined by light and electron microscopy, and immunohistochemistry. Reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) using enhanced real-time PCR was applied to look for evidence of SARS-associated coronavirus infection. Marked accumulation of cells in mitosis was observed in two patients and apoptosis was observed in all three patients. Other common pathologic features included ballooning of hepatocytes and mild to moderate lobular lymphocytic infiltration. No eosinophilic infiltration, granuloma, cholestasis, fibrosis, or fibrin deposition was noted. Immunohistochemical studies revealed 0.5% to 11.4% of nuclei were positive for proliferative antigen Ki-67. RT-PCR showed evidence of SARS-associated coronavirus in the liver tissues, but not in the sera of all 3 patients. However, electron microscopy could not identify viral particles. No giant mitochondria, micro- or macro-vesicular steatosis was observed. In conclusion, hepatic impairment in patients with SARS is due to SARS-associated coronavirus infection of the liver. The prominence of mitotic activity of hepatocytes is unique and may be due to a hyperproliferative state with or without disruption of cell cycle by the coronavirus. With better knowledge of pathogenesis, specific therapy may be targeted to reduce viral replication and modify the disease course.
Figures


Comment in
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome and the liver.Hepatology. 2004 Feb;39(2):291-4. doi: 10.1002/hep.20069. Hepatology. 2004. PMID: 14767979 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Holmes KV, Lai MMC. Coronaviridae and their replication. In: Fields B, Knipe D, Howley P, eds. Fields virology. 3rd edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott‐Raven, 1996: 1075.
-
- Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, van der Werf S, Brodt HR, Becker S, Rabenau H, et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1967–1976. - PubMed
-
- Lee N, Hui D, Wu A, Chan P, Cameron P, Joynt GM, Ahuja A, et al. A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1986–1994. - PubMed
-
- Tsang KW, Ho PL, Ooi GC, Yee WK, Wang T, Chan‐Yeung M, Lam WK, et al. A cluster of cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1977–1985. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
