Regulated exocytosis of GABA-containing synaptic-like microvesicles in pancreatic beta-cells
- PMID: 14769845
- PMCID: PMC2217446
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200308966
Regulated exocytosis of GABA-containing synaptic-like microvesicles in pancreatic beta-cells
Abstract
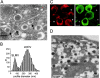
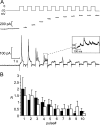
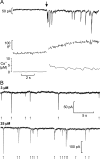
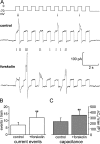
We have explored whether gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is released by regulated exocytosis of GABA-containing synaptic-like microvesicles (SLMVs) in insulin-releasing rat pancreatic beta-cells. To this end, beta-cells were engineered to express GABA(A)-receptor Cl(-)-channels at high density using adenoviral infection. Electron microscopy indicated that the average diameter of the SLMVs is 90 nm, that every beta-cell contains approximately 3,500 such vesicles, and that insulin-containing large dense core vesicles exclude GABA. Quantal release of GABA, seen as rapidly activating and deactivating Cl(-)-currents, was observed during membrane depolarizations from -70 mV to voltages beyond -40 mV or when Ca(2+) was dialysed into the cell interior. Depolarization-evoked GABA release was suppressed when Ca(2+) entry was inhibited using Cd(2+). Analysis of the kinetics of GABA release revealed that GABA-containing vesicles can be divided into a readily releasable pool and a reserve pool. Simultaneous measurements of GABA release and cell capacitance indicated that exocytosis of SLMVs contributes approximately 1% of the capacitance signal. Mathematical analysis of the release events suggests that every SLMV contains 0.36 amol of GABA. We conclude that there are two parallel pathways of exocytosis in pancreatic beta-cells and that release of GABA may accordingly be temporally and spatially separated from insulin secretion. This provides a basis for paracrine GABAergic signaling within the islet.
Figures




References
-
- Ahnert-Hilger, G., and B. Wiedenmann. 1992. The amphicrine pancreatic cell line, AR42J, secretes GABA and amylase by separate regulated pathways. FEBS Lett. 314:41–44. - PubMed
-
- Albillos, A., G. Dernick, H. Horstmann, W. Almers, G. Alvarez de Toledo, and M. Lindau. 1997. The exocytotic event in chromaffin cells revealed by patch amperometry. Nature. 389:509–512. - PubMed
-
- Amatore, C., Y. Bouret, E.R. Travis, and R.M. Wightman. 2000. Interplay between membrane dynamics, diffusion and swelling pressure governs individual vesicular exocytotic events during release of adrenaline by chromaffin cells. Biochimie. 82:481–496. - PubMed
-
- Ämmälä, C., F.M. Ashcroft, and P. Rorsman. 1993. Calcium-independent potentiation of insulin release by cyclic AMP in single β-cells. Nature. 363:356–358. - PubMed
-
- Antunes, C.M., A.P. Salgado, L.M. Rosario, and R.M. Santos. 2000. Differential patterns of glucose-induced electrical activity and intracellular calcium responses in single mouse and rat pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 49:2028–2038. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

