Distribution of prostaglandin E2 in gastric and duodenal mucosa: possible role in the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer
- PMID: 1477025
- PMCID: PMC4532093
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1992.7.1.1
Distribution of prostaglandin E2 in gastric and duodenal mucosa: possible role in the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer
Abstract
Background: Prostaglandin E which is present abundantly in the gastric mucosa is a powerful inhibitor of gastric acid secretion and a stimulus to gastric mucus production. In addition, prostaglandin E2 inhibits ulcer formation in animals, and the synthetic analogues of prostaglandin E have successfully been used in the treatment of patients with gastric and duodenal ulcer disease. To evaluate the role of endogenous prostaglandin E2 in the pathogenesis of the peptic ulcer disease, we measured mucosal prostaglandin E2 levels in patients with gastric and duodenal ulcer disease and compared with that of non-ulcer control persons.
Methods: The study population was made up of 44 non-ulcer persons, 36 patients with a benign gastric ulcer, and 48 with a duodenal ulcer. Every mucosal specimen, taken from the antrum and from the duodenal bulb, were homogenized, mixed with 1 M HCl, and centrifuged. After removal of the supernatant, precipitate was eluted with ethyl acetate in the Amprep C18 minicolumn. Then the extracted prostaglandin E2 in the ethyl acetate fractions was converted into its methyl oximate derivatives, and the prostaglandin E2 level was measured by radioimmunoassay. During the procedure any homogenized specimen which was looking grossly bloody was removed from the assay in order to avoid any possible contamination or prostaglandin E2 in blood.
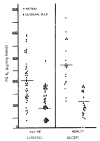
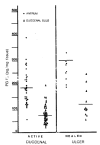
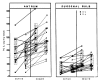
Results: In non-ulcer persons, the mean values was 258.17 +/- 127.03 pg/mg. tissue in antrum and 121.07 +/- 67.46 pg/mg. tissue in duodenal bulb. The corresponding values were 186.42 +/- 70.51 pg/mg. tissue, 79.44 +/- 39.04 pg/mg. tissue in gastric ulcer patients and 204. 94 92.03 pg/mg. tissue, 99.66 +/- 56.10 pg/mgl. tissue in duodenal ulcer patients respectively. Gastric ulcer patients have the significantly lower level of the antral and duodenal prostaglandin E2 (p < 0.005). Those levels of duodenal ulcer patients were also significantly lower than those of non-ulcer persons (p < 0.025 & 0.05). Antral prostaglandin E2 level increased to 305.21 +/- 104.91 pg/mg. tissue in the gastric ulcer patients (p < 0.005) and to 271.02 +/- 93. 23 pg/mg. tissue in the duodenal ulcer (p < 0.005) when the ulcer crater was healed. The duodenal bulb prostaglandin E2 level was also increased in the healed stage of ulcer, e. g., 128.84 +/- 57.62 (p < 0.005) and 112.60 +/- 42.25 pg/mg. tissue, respectively.
Conclusion: These results suggest that prostaglandin deficiency in the antral and duodenal bulb mucosa may have an important role in the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
G- and D-cell populations, serum and tissue concentrations of gastrin and somatostatin in patients with peptic ulcer diseases.Korean J Intern Med. 1993 Jan;8(1):1-7. doi: 10.3904/kjim.1993.8.1.1. Korean J Intern Med. 1993. PMID: 7903552 Free PMC article.
-
Duodenal and antral mucosal prostaglandin E2 synthesis in a study of normal subjects and all stages of duodenal ulcer disease treated by H2 receptor antagonists.Gut. 1989 Feb;30(2):161-5. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.2.161. Gut. 1989. PMID: 2564833 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 and F2 alpha levels in the duodenal and antral mucosa of non-ulcer dyspeptic and duodenal ulcer patients.Hepatogastroenterology. 1990 Apr;37(2):208-11. Hepatogastroenterology. 1990. PMID: 2341116
-
Defects in prostaglandin synthesis and metabolism in ulcer disease.Dig Dis Sci. 1986 Feb;31(2 Suppl):20S-27S. doi: 10.1007/BF01309318. Dig Dis Sci. 1986. PMID: 3510842 Review.
-
The energy systems of gastric tissues, their neural, hormonal and pharmacological regulations in order to gastric H+ secretion and ulcerogenesis. (A review of animal experiments and clinical biochemical studies).Acta Med Acad Sci Hung. 1979;36(1):1-29. Acta Med Acad Sci Hung. 1979. PMID: 230686 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Potency of Gardenia Extract Against H. pylori: Insights from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 2;13(1):92. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010092. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheung LY, Jubiz W, Moore JG. Gastric prostaglandin E output during basal and stimulated acid secretion in normal subjects and patients with duodenal ulcer. J Sur Res. 1976;20:369. - PubMed
-
- Wilson DE, PHilips C, Levine RA. Inhibition of gastric secretion in man by prostaglandin A2. Gastroenterology. 1971;61:201. - PubMed
-
- Carter DC, Karim SMM, Bhana D, Ganesan PA. Inhibition of human gastric secretion by prostaglandin. Brit J Surg. 1973;60:828. - PubMed
-
- Salmon JA, Karim SMM, Carter DC, Adaikan PG, Bhana D. Effect of 15 (R) 15-Methyl Prostglandin E2 methyl ester on basal and pentagastrin stimulated pepsin secretion in man. International Research Communications System, Medical Science. 1975;3:83.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
