Effects of low dose ramipril on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and raised excretion of urinary albumin: randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial (the DIABHYCAR study)
- PMID: 14960504
- PMCID: PMC351842
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.37970.629537.0D
Effects of low dose ramipril on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and raised excretion of urinary albumin: randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial (the DIABHYCAR study)
Erratum in
- BMJ. 2004 Mar 20;328(7441):686
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether a low dose of the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor ramipril lowers cardiovascular and renal events in patients with type 2 diabetes who have microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
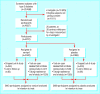
Design: Randomised, double blind, parallel group trial comparing ramipril (1.25 mg/day) with placebo (on top of usual treatment) for cardiovascular and renal outcomes for at least three years.
Setting: Multicentre, primary care study conducted mostly by general practitioners in 16 European and north African countries.
Participants: 4912 patients with type 2 diabetes aged >50 years who use oral antidiabetic drugs and have persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria (urinary albumin excretion > or = 20 mg/l in two consecutive samples), and serum creatinine < or = 150 micromol/l.
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome measure was the combined incidence of cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure leading to hospital admission, and end stage renal failure.
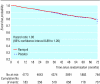
Results: Participants were followed for 3 to 6 (median 4) years. There were 362 primary events among the 2443 participants taking ramipril (37.8 per 1000 patient years) and 377 events among the 2469 participants taking placebo (38.8 per 1000 patient years; hazard ratio 1.03 (95% confidence interval 0.89 to 1.20, P = 0.65)). None of the components of the primary outcome was reduced. Ramipril lowered systolic and diastolic blood pressures (by 2.43 and 1.06 mm Hg respectively after two years) and favoured regression from microalbuminuria (20-200 mg/l) or proteinuria (> 200mg/l) to normal level (< 20 mg/l) or microalbuminuria (P < 0.07) in 1868 participants who completed the study.
Conclusions: Low dose (1.25 mg) ramipril once daily has no effect on cardiovascular and renal outcomes of patients with type 2 diabetes and albuminuria, despite a slight decrease in blood pressure and urinary albumin. The cardiovascular benefits of a daily higher dose (10 mg) ramipril observed elsewhere are not found with an eightfold lower daily dose.
Figures
Comment in
-
Clinical trials report. angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in diabetes: above and beyond the beneficial effect of blood pressure?Curr Hypertens Rep. 2004 Oct;6(5):366-8. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2004. PMID: 15341689 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mogensen CE. Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med 1984;310: 356-60. - PubMed
-
- Jarrett RJ, Viberti GC, Argyropoulos A, Hill RD, Mahmud U, Murrels TJ. Microalbuminuria predicts mortality in non insulin-dependent diabetics. Diabet Med 1984;1: 17-9. - PubMed
-
- Mogensen CE. Microalbuminuria, blood pressure and diabetic renal disease: origin and development of ideas. Diabetologia 1999;42: 263-85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous