A novel DNA enzyme reduces glycosaminoglycan chains in the glial scar and allows microtransplanted dorsal root ganglia axons to regenerate beyond lesions in the spinal cord
- PMID: 14960611
- PMCID: PMC6730336
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4986-03.2004
A novel DNA enzyme reduces glycosaminoglycan chains in the glial scar and allows microtransplanted dorsal root ganglia axons to regenerate beyond lesions in the spinal cord
Abstract
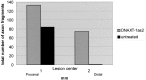
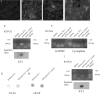
CNS lesions induce production of ECM molecules that inhibit axon regeneration. One major inhibitory family is the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs). Reduction of their glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains with chondroitinase ABC leads to increased axon regeneration that does not extend well past the lesion. Chondroitinase ABC, however, is unable to completely digest the GAG chains from the protein core, leaving an inhibitory "stub" carbohydrate behind. We used a newly designed DNA enzyme, which targets the mRNA of a critical enzyme that initiates glycosylation of the protein backbone of PGs, xylosyltransferase-1. DNA enzyme administration to TGF-beta-stimulated astrocytes in culture reduced specific GAG chains. The same DNA enzyme applied to the injured spinal cord led to a strong reduction of the GAG chains in the lesion penumbra and allowed axons to regenerate around the core of the lesion. Our experiments demonstrate the critical role of PGs, and particularly those in the penumbra, in causing regeneration failure in the adult spinal cord.
Figures

References
-
- Bradbury EJ, Moon LD, Popat RJ, King VR, Bennett GS, Patel PN, Fawcett JW, McMahon SB (2002) Chondroitinase ABC promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature 416: 636-640. - PubMed
-
- Brose K, Bland KS, Wang KH, Arnott D, Henzel W, Goodman CS, Tessier-Lavigne M, Kidd T (1999) Slit proteins bind Robo receptors and have an evolutionarily conserved role in repulsive axon guidance. Cell 96: 795-806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
