A gephyrin-related mechanism restraining glycine receptor anchoring at GABAergic synapses
- PMID: 14960612
- PMCID: PMC6730342
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4260-03.2004
A gephyrin-related mechanism restraining glycine receptor anchoring at GABAergic synapses
Abstract
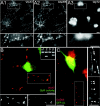
Spinal cord neurons release glycine and GABA and accumulate glycine receptors (GlyRs) and GABA(A) receptors in the same postsynaptic densities. In contrast, supramedullar neurons prefer GABA as a neurotransmitter and exclude GlyRs from postsynaptic anchoring. The general aim of the present study was to elucidate the mechanisms underlying transmitter-appropriate receptor accumulation at inhibitory synapses. Specifically, we intended to clarify the molecular basis for the prohibition of GlyR accumulation in the postsynaptic densities of GABAergic synapses. A green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged gephyrin-binding loop of the GlyR beta subunit (GFP::betaL) was used as a surrogate for full-length receptors to characterize the GlyR binding capacity of postsynaptic gephyrins in transfected neurons. Both in spinal cord neurons (SCNs) and hippocampal neurons (HNs) GFP::betaL distribution displayed transmitter specificity; i.e., postsynaptic accumulation of GFP::betaL was high opposite terminals able to release glycine and low opposite purely GABAergic terminals. When comparing SCN and HN cultures we found that the level of mRNA coding for gephyrin splice variants containing the cassette C5 (C5-gephyrins) was significantly higher in HNs. In HNs depleted of C5-gephyrins, both GFP::betaL and endogenous GlyRs accumulated at postsynaptic GABAergic sites. Accordingly in SCNs, GFP-tagged C5-gephyrin displayed a preferential postsynaptic accumulation opposite GABAergic synapses. Comparison of glycinergic, mixed, and GABAergic synapses in SCNs showed that the degree of GlyR accumulation was inversely related to the amount of postsynaptic C5-gephyrin. These results identify the C5 splice variant of gephyrin as a factor regulating the transmitter-appropriate degree of GlyR accumulation at inhibitory synapses.
Figures






References
-
- Beaulieu C, Campistron G, Crevier C (1994) Quantitative aspects of the GABA circuitry in the primary visual cortex of the adult rat. J Comp Neurol 339: 559-572. - PubMed
-
- Brewer GJ, Cotman CW (1989) Survival and growth of hippocampal neurons in defined medium at low density: advantages of a sandwich culture technique or low oxygen. Brain Res 494: 65-74. - PubMed
-
- Butler MH, Hayashi A, Ohkoshi N, Villmann C, Becker CM, Feng G, De Camilli P, Solimena M (2000) Autoimmunity to gephyrin in Stiff-Man syndrome. Neuron 26: 307-312. - PubMed
-
- David-Watine B (2001) The human gephyrin (GPHN) gene: structure, chromosome localization and expression in non-neuronal cells. Gene 271: 239-245. - PubMed
-
- Dumoulin A, Rostaing P, Bedet C, Levi S, Isambert MF, Henry JP, Triller A, Gasnier B (1999) Presence of the vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter in GABAergic and glycinergic synaptic terminal boutons. J Cell Sci 112: 811-823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
