Human CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells control T-cell responses to human immunodeficiency virus and cytomegalovirus antigens
- PMID: 14963140
- PMCID: PMC369239
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.5.2454-2459.2004
Human CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells control T-cell responses to human immunodeficiency virus and cytomegalovirus antigens
Abstract
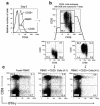
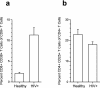
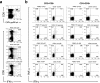
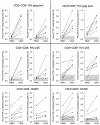
Regulatory T (T(R)) cells maintain tolerance to self-antigens and control immune responses to alloantigens after organ transplantation. Here, we show that CD4(+) CD25(+) human T(R) cells suppress virus-specific T-cell responses. Depletion of T(R) cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells enhances T-cell responses to cytomegalovirus and human immunodeficiency virus antigens. We propose that chronic viral infections lead to induction of suppressive T(R) cells that inhibit the antiviral immune response.
Figures
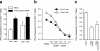
References
-
- Baecher-Allan, C., J. A. Brown, G. J. Freeman, and D. A. Hafler. 2001. CD4+CD25high regulatory cells in human peripheral blood. J. Immunol. 167:1245-1253. - PubMed
-
- Belkaid, Y., C. A. Piccirillo, S. Mendez, E. M. Shevach, and D. L. Sacks. 2002. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells control Leishmania major persistence and immunity. Nature 420:502-507. - PubMed
-
- Bluestone, J. A., and A. K. Abbas. 2003. Opinion-regulatory lymphocytes: natural versus adaptive regulatory T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:253-257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

