Gibberellins repress photomorphogenesis in darkness
- PMID: 14963246
- PMCID: PMC389929
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.035451
Gibberellins repress photomorphogenesis in darkness
Abstract
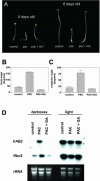
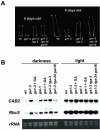
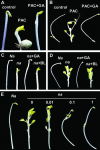
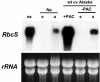
Plants undergo two different developmental programs depending on whether they are growing in darkness (skotomorphogenesis) or in the presence of light (photomorphogenesis). It has been proposed that the latter is the default pathway followed by many plants after germination and before the seedling emerges from soil. The transition between the two pathways is tightly regulated. The conserved COP1-based complex is central in the light-dependent repression of photomorphogenesis in darkness. Besides this control, hormones such as brassinosteroids (BRs), cytokinins, auxins, or ethylene also have been shown to regulate, to different extents, this developmental switch. In the present work, we show that the hormone gibberellin (GA) widely participates in this regulation. Studies from Arabidopsis show that both chemical and genetic reductions of endogenous GA levels partially derepress photomorphogenesis in darkness. This is based both on morphological phenotypes, such as hypocotyl elongation and hook and cotyledon opening, and on molecular phenotypes, such as misregulation of the light-controlled genes CAB2 and RbcS. Genetic studies indicate that the GA signaling elements GAI and RGA participate in these responses. Our results also suggest that GA regulation of this response partially depends on BRs. This regulation seems to be conserved across species because lowering endogenous GA levels in pea (Pisum sativum) induces full de-etiolation in darkness, which is not reverted by BR application. Our results, therefore, attribute an important role for GAs in the establishment of etiolated growth and in repression of photomorphogenesis.
Figures
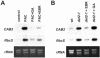
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

