Cost of an emerging epidemic: an economic analysis of atrial fibrillation in the UK
- PMID: 14966048
- PMCID: PMC1768125
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2002.008748
Cost of an emerging epidemic: an economic analysis of atrial fibrillation in the UK
Erratum in
- Heart. 2007 Nov;93(11):1472. Murphy, N [corrected to Murphy, N F]
Abstract
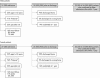
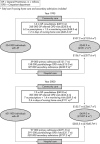
Objective: To evaluate the cost of atrial fibrillation (AF) to health and social services in the UK in 1995 and, based on epidemiological trends, to project this estimate to 2000. DESIGN, SETTING, AND MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES: Contemporary estimates of health care activity related to AF were applied to the whole population of the UK on an age and sex specific basis for the year 1995. The activities considered (and costs calculated) were hospital admissions, outpatient consultations, general practice consultations, and drug treatment (including the cost of monitoring anticoagulant treatment). By adjusting for the progressive aging of the British population and related increases in hospital admissions, the cost of AF was also projected to the year 2000.
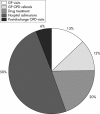
Results: There were 534 000 people with AF in the UK during 1995. The "direct" cost of health care for these patients was 244 million pounds sterling (approximately 350 million euros) or 0.62% of total National Health Service (NHS) expenditure. Hospitalisations and drug prescriptions accounted for 50% and 20% of this expenditure, respectively. Long term nursing home care after hospital admission cost an additional 46.4 million pounds sterling (approximately 66 million euros). The direct cost of AF rose to 459 million pounds sterling (approximately 655 million euros) in 2000, equivalent to 0.97% of total NHS expenditure based on 1995 figures. Nursing home costs rose to 111 million pounds sterling (approximately 160 million euros).
Conclusions: AF is an extremely costly public health problem.
Figures

Comment in
-
Atrial fibrillation: an emerging epidemic?Heart. 2004 Mar;90(3):239-40. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2003.014720. Heart. 2004. PMID: 14966028 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ezekowitz MD. Atrial fibrillation: the epidemic of the new millennium. Ann Intern Med 1999;131:537–8. - PubMed
-
- Ryder KM, Benjamin EJ. Epidemiology and significance of atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 1998;84:131R–8R. - PubMed
-
- Sudlow M, Thomson R, Thwaites B, et al. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation and eligibility for anticoagulants in the community. Lancet 1998;352:1167–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
