An intronic enhancer regulates splicing of the twintron of Drosophila melanogaster prospero pre-mRNA by two different spliceosomes
- PMID: 14966268
- PMCID: PMC350559
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.1855-1869.2004
An intronic enhancer regulates splicing of the twintron of Drosophila melanogaster prospero pre-mRNA by two different spliceosomes
Abstract
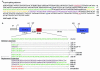
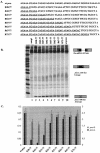
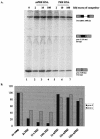
We have examined the alternative splicing of the Drosophila melanogaster prospero twintron, which contains splice sites for both the U2- and U12-type spliceosome and generates two forms of mRNA, pros-L (U2-type product) and pros-S (U12-type product). We find that twintron splicing is developmentally regulated: pros-L is abundant in early embryogenesis while pros-S displays the opposite pattern. We have established a Kc cell in vitro splicing system that accurately splices a minimal pros substrate containing the twintron and have examined the sequence requirements for pros twintron splicing. Systematic deletion and mutation analysis of intron sequences established that twintron splicing requires a 46-nucleotide purine-rich element located 32 nucleotides downstream of the U2-type 5' splice site. While this element regulates both splicing pathways, its alteration showed the severest effects on the U2-type splicing pathway. Addition of an RNA competitor containing the wild-type purine-rich element to the Kc extract abolished U2-type splicing and slightly repressed U12-type splicing, suggesting that a trans-acting factor(s) binds the enhancer element to stimulate twintron splicing. Thus, we have identified an intron region critical for prospero twintron splicing as a first step towards elucidating the molecular mechanism of splicing regulation involving competition between the two kinds of spliceosomes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Drosophila hnRNP A1 homologs Hrp36/Hrp38 enhance U2-type versus U12-type splicing to regulate alternative splicing of the prospero twintron.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Feb 24;106(8):2577-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812826106. Epub 2009 Feb 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19196985 Free PMC article.
-
The divergent U12-type spliceosome is required for pre-mRNA splicing and is essential for development in Drosophila.Mol Cell. 2002 Feb;9(2):439-46. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00441-0. Mol Cell. 2002. PMID: 11864616
-
RS domain-splicing signal interactions in splicing of U12-type and U2-type introns.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Jul;14(7):597-603. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1263. Epub 2007 Jul 1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17603499
-
Splicing of a rare class of introns by the U12-dependent spliceosome.Biol Chem. 2005 Aug;386(8):713-24. doi: 10.1515/BC.2005.084. Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16201866 Review.
-
Minor Intron Splicing from Basic Science to Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 4;22(11):6062. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116062. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34199764 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The carboxyl termini of RAN translated GGGGCC nucleotide repeat expansions modulate toxicity in models of ALS/FTD.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020 Aug 4;8(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s40478-020-01002-8. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020. PMID: 32753055 Free PMC article.
-
Minor intron splicing revisited: identification of new minor intron-containing genes and tissue-dependent retention and alternative splicing of minor introns.BMC Genomics. 2019 Aug 30;20(1):686. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6046-x. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31470809 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational analysis of the U12-dependent branch site consensus sequence.RNA. 2008 Nov;14(11):2430-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.1189008. Epub 2008 Sep 29. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18824513 Free PMC article.
-
Surprisingly high number of Twintrons in vertebrates.Biol Direct. 2013 Jan 28;8:4. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-8-4. Biol Direct. 2013. PMID: 23356793 Free PMC article.
-
The significant other: splicing by the minor spliceosome.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):61-76. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1141. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013. PMID: 23074130 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andres, A. J., and P. Cherbas. 1992. Tissue-specific ecdysone responses: regulation of the Drosophila genes Eip28/29 and Eip40 during larval development. Development 116:865-876. - PubMed
-
- Black, D. L. 1992. Activation of c-src neuron-specific splicing by an unusual RNA element in vivo and in vitro. Cell 69:795-807. - PubMed
-
- Burge, C. B., T. Tuschl, and P. A. Sharp. 1999. The nature of modern RNA suggests a prebiotic RNA, p. 525-560. In R. F. Gesteland, T. Cech, and J. F. Atkins (ed.), RNA world. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
