Barrier proteins remodel and modify chromatin to restrict silenced domains
- PMID: 14966276
- PMCID: PMC350565
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.1956-1967.2004
Barrier proteins remodel and modify chromatin to restrict silenced domains
Abstract
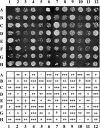
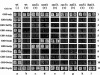
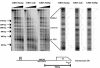
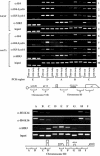
Transcriptionally active and inactive domains are frequently found adjacent to one another in the eukaryotic nucleus. To better understand the underlying mechanisms by which domains maintain opposing transcription patterns, we performed a systematic genomewide screen for proteins that may block the spread of silencing in yeast. This analysis identified numerous proteins with efficient silencing blocking activities, and some of these have previously been shown to be involved in chromatin dynamics. We isolated subunits of Swi/Snf, mediator, and TFIID, as well as subunits of the Sas-I, SAGA, NuA3, NuA4, Spt10p, Rad6p, and Dot1p complexes, as barrier proteins. We demonstrate that histone acetylation and chromatin remodeling occurred at the barrier and correlated with a block to the spread of silencing. Our data suggest that multiple overlapping mechanisms were involved in delimiting silenced and active domains in vivo.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The silencing complex SAS-I links histone acetylation to the assembly of repressed chromatin by CAF-I and Asf1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genes Dev. 2001 Dec 1;15(23):3169-82. doi: 10.1101/gad.929001. Genes Dev. 2001. PMID: 11731480 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of boundaries of transcriptionally silent chromatin by nucleosome-excluding structures.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Mar;24(5):2118-31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.2118-2131.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14966290 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the nucleoporin Nup170p in chromatin structure and gene silencing.Cell. 2013 Feb 28;152(5):969-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.049. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23452847 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin and transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1999 Jul;23(4):503-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1999.tb00410.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10422263 Review.
-
Recruitment of chromatin remodelling factors during gene activation via the glucocorticoid receptor N-terminal domain.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):410-4. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961930 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone H1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae inhibits transcriptional silencing.Genetics. 2006 Jun;173(2):579-87. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.050195. Epub 2006 Apr 2. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16582449 Free PMC article.
-
Rpd3-dependent boundary formation at telomeres by removal of Sir2 substrate.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Mar 23;107(12):5522-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909169107. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133733 Free PMC article.
-
The role of insulator elements in large-scale chromatin structure in interphase.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2007 Oct;18(5):682-90. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2007.08.009. Epub 2007 Aug 25. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17919949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone modifications influence mediator interactions with chromatin.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Oct;39(19):8342-54. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr551. Epub 2011 Jul 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21742760 Free PMC article.
-
Spt3 and Spt8 Are Involved in the Formation of a Silencing Boundary by Interacting with TATA-Binding Protein.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 30;13(4):619. doi: 10.3390/biom13040619. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham, J., K. A. Nasmyth, J. N. Strathern, A. J. Klar, and J. B. Hicks. 1984. Regulation of mating-type information in yeast. Negative control requiring sequences both 5′ and 3′ to the regulated region. J. Mol. Biol. 176:307-331. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio, O. M., and D. E. Gottschling. 1994. Overcoming telomeric silencing: a trans-activator competes to establish gene expression in a cell cycle-dependent way. Genes Dev. 8:1133-1146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
