Modulation of plasma membrane calcium-ATPase activity by local calcium microdomains near CRAC channels in human T cells
- PMID: 14966303
- PMCID: PMC1665005
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.060004
Modulation of plasma membrane calcium-ATPase activity by local calcium microdomains near CRAC channels in human T cells
Abstract
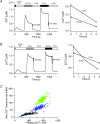
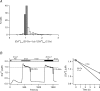
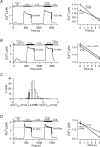
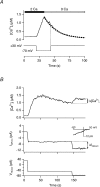
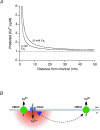
The spatial distribution of Ca(2+) signalling molecules is critical for establishing specific interactions that control Ca(2+) signal generation and transduction. In many cells, close physical coupling of Ca(2+) channels and their targets enables precise and robust activation of effector molecules through local [Ca(2+)](i) elevation in microdomains. In T cells, the plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase (PMCA) is a major target of Ca(2+) influx through Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) (CRAC) channels. Elevation of [Ca(2+)](i) slowly modulates pump activity to ensure the stability and enhance the dynamic nature of Ca(2+) signals. In this study we probed the functional organization of PMCA and CRAC channels in T cells by manipulating Ca(2+) microdomains near CRAC channels and measuring the resultant modulation of PMCAs. The amplitude and spatial extent of microdomains was increased by elevating the rate of Ca(2+) entry, either by raising extracellular [Ca(2+)], by increasing the activity of CRAC channels with 2-aminoethoxyborane (2-APB), or by hyperpolarizing the plasma membrane. Surprisingly, doubling the rate of Ca(2+) influx does not further increase global [Ca(2+)](i) in a substantial fraction of cells, due to a compensatory increase in PMCA activity. The enhancement of PMCA activity without changes in global [Ca(2+)](i) suggests that local [Ca(2+)](i) microdomains near CRAC channels effectively promote PMCA modulation. These results reveal an intimate functional association between CRAC channels and Ca(2+) pumps in the plasma membrane which may play an important role in governing the time course and magnitude of Ca(2+) signals in T cells.
Figures

References
-
- Almers W, Neher E. The Ca signal from fura-2 loaded mast cells depends strongly on the method of dye-loading. FEBS Lett. 1985;192:13–18. - PubMed
-
- Apicella S, Chen S, Bing R, Penniston JT, Llinas R, Hillman DE. Plasmalemmal ATPase calcium pump localizes to inner and outer hair bundles. Neuroscience. 1997;79:1145–1151. - PubMed
-
- Augustine GJ, Neher E. Neuronal Ca2+ signalling takes the local route. Curr Op Neurobiol. 1992;2:302–307. - PubMed
-
- Bakowski D, Parekh AB. Monovalent cation permeability and Ca2+ block of the store-operated Ca2+ current ICRAC in rat basophilic leukemia cells. Pflugers Arch. 2002;443:892–902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

