Increasing prevalence of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, expanded-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, and imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Korea: KONSAR study in 2001
- PMID: 14966334
- PMCID: PMC2822269
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.1.8
Increasing prevalence of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, expanded-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, and imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Korea: KONSAR study in 2001
Abstract
The 5th year KONSAR surveillance in 2001 was based on routine test data at 30 participating hospitals. It was of particular interest to find a trend in the resistances of enterococci to vancomycin, of Enterobacteriaceae to the 3rd generation cephalosporin and fluoroquinolone, and of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and acinetobacters to carbapenem. Resistance rates of Gram-positive cocci were: 70% of Staphylococcus aureus to oxacillin; 88% and 16% of Enterococcus faecium to ampicillin and vancomycin, respectively. Seventy-two percent of pneumococci were nonsusceptible to penicillin. The resistance rates of Enterobacteriaceae were: Escherichia coli, 28% to fluoroquinolone; Klebsiella pneumoniae, 27% to ceftazidime, and 20% to cefoxitin; and Enterobacter cloacae, > or =40% to cefotaxime and ceftazidime. The resistance rates of P. aeruginosa were 21% to ceftazidime, 17% to imipenem, and those of the acinetobacters were > or =61% to ceftazidime, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolone and cotrimoxazole. Thirty-five percent of non-typhoidal salmonellae were ampicillin resistant, and 66% of Haemophilus influenzae were beta-lactamase producers. Notable changes over the 1997-2001 period were: increases in vancomycin-resistant E. faecium, and amikacin- and fluoroquinolone-resistant acinetobacters. With the increasing prevalence of resistant bacteria, nationwide surveillance has become more important for optimal patient management, for the control of nosocomial infection, and for the conservation of the newer antimicrobial agents.
Figures

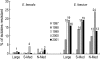

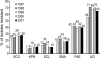
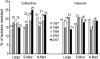
Similar articles
-
Increasing prevalence of vancomycin-resistant enterococci, and cefoxitin-, imipenem- and fluoroquinolone-resistant gram-negative bacilli: a KONSAR study in 2002.Yonsei Med J. 2004 Aug 31;45(4):598-608. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2004.45.4.598. Yonsei Med J. 2004. PMID: 15344199
-
High prevalence of ceftazidime-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and increase of imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter spp. in Korea: a KONSAR program in 2004.Yonsei Med J. 2006 Oct 31;47(5):634-45. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.5.634. Yonsei Med J. 2006. PMID: 17066507 Free PMC article.
-
Further increase of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, amikacin- and fluoroquinolone-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, and imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter spp. in Korea: 2003 KONSAR surveillance.Yonsei Med J. 2006 Feb 28;47(1):43-54. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.1.43. Yonsei Med J. 2006. PMID: 16502484 Free PMC article.
-
Present situation of antimicrobial resistance in Korea.J Infect Chemother. 2000 Dec;6(4):189-95. doi: 10.1007/s101560070001. J Infect Chemother. 2000. PMID: 11810564 Review.
-
Multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus: Three major threats to hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients.Transpl Infect Dis. 2017 Dec;19(6):10.1111/tid.12762. doi: 10.1111/tid.12762. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Transpl Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28815897 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitogenic response and probiotic characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolated from indigenously pickled vegetables and fermented beverages.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Feb;28(2):703-11. doi: 10.1007/s11274-011-0866-4. Epub 2011 Sep 14. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22806866
-
Vancomycin-resistant enterococcal bacteremia in a hematology unit: molecular epidemiology and analysis of clinical course.J Korean Med Sci. 2005 Apr;20(2):169-76. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.2.169. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. PMID: 15831982 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Clinical Factors Associated with Medical Burden and Functional Status in Pyogenic Spine Infection.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 28;12(7):2551. doi: 10.3390/jcm12072551. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37048635 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and control of an outbreak of vancomycin-resistant enterococci in the intensive care units.Yonsei Med J. 2009 Oct 31;50(5):637-43. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.5.637. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Yonsei Med J. 2009. PMID: 19881966 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between virulence genotype and fluoroquinolone resistance in carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Ann Lab Med. 2014 Jul;34(4):286-92. doi: 10.3343/alm.2014.34.4.286. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Ann Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 24982833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hunter PA, Reeves DS. The current status of surveillance of resistance to antimicrobial agents: report on a meeting. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002;49:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Cosgrove SE, Carmeli Y. The impact of antimicrobial resistance on health and economic outcomes. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:1433–1437. - PubMed
-
- Voss A, Milatovic D, Wallrauch-Schwarz C, Rosdahl VT, Braveny I. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Europe. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1994;13:50–55. - PubMed
-
- Sorberg M, Farra A, Ransjo U, Gardlund B, Rylander M, Settergren B, Kalin M, Kronvall G. Different trends in antibiotic resistance rates at a university teaching hospital. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2003;9:388–396. - PubMed
-
- Morris AK, Masterton RG. Antibiotic resistance surveillance: action for international studies. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002;49:7–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

