Transfection efficiency of pORF lacZ plasmid lipopolyplex to hepatocytes and hepatoma cells
- PMID: 14966911
- PMCID: PMC4716974
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i4.531
Transfection efficiency of pORF lacZ plasmid lipopolyplex to hepatocytes and hepatoma cells
Abstract
Aim: To develop a novel non-viral gene delivery system, which has a small particle size and a high transfection efficiency to hepatocyte and hepatoma cells.
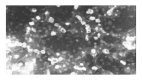
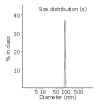
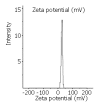
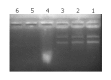
Methods: Lipid-polycation-DNA lipopolyplex (LPD) was prepared by mixing plasmid DNA and polylysine. The resulted polyplex was incubated for 10 min at room temperature, following the addition of preformed cationic liposomes. The morphology of LPD was observed by transmission electron microscopy. The diameter and surface charge of LPD were measured by photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS). The nuclease protection ability of LPD was evaluated by agarose gel electrophoresis. Estimation of the transfection efficiency was performed by galactosidase assay in Chang cells and SMMC-7721 cells.
Results: LPD had a regular spherical surface. The average diameter and the zeta potential of LPD were 132.1 nm and 26.8 mV respectively. LPD could protect plasmid DNA from nuclease degradation after 2 hours incubation at 37 degrees while the naked DNA degraded rapidly. The average transfection efficiencies were 86.2+/-8.9% and 72.4+/-6.5% in Chang cells and SMMC-7721 cells respectively.
Conclusion: LPD has a rather small particle size and a high transfection activity. LPD may be a good non-viral vector for application in some gene delivery.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Preparation of lipid-protamine-DNA complexes and evaluation of their transfection efficiencies in vitro].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2004 Oct;39(10):792-6. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2004. PMID: 15700818 Chinese.
-
[Preparation and gene expression of transferrin modified gene loaded procationic liposomes].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007 Feb;42(2):216-20. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17518055 Chinese.
-
[Transfection efficiency comparison of cationic liposome-DNA complexes and lipid-protamine-DNA complexes in vitro].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Feb;24(1):191-5. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 17333920 Chinese.
-
Optimizing the novel formulation of liposome-polycation-DNA complexes (LPD) by central composite design.Arch Pharm Res. 2004 Jul;27(7):797-805. doi: 10.1007/BF02980151. Arch Pharm Res. 2004. PMID: 15357010
-
Lipopolyplex for Therapeutic Gene Delivery and Its Application for the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2016 Apr 5;8:68. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00068. eCollection 2016. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27092073 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pouton CW, Seymour LW. Key issues in non-viral gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;46:187–203. - PubMed
-
- Liu F, Huang L. Development of non-viral vectors for systemic gene delivery. J Control Release. 2002;78:259–266. - PubMed
-
- Nishikawa M, Huang L. Nonviral vectors in the new millennium: delivery barriers in gene transfer. Hum Gene Ther. 2001;12:861–870. - PubMed
-
- Davis ME. Non-viral gene delivery systems. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2002;13:128–131. - PubMed
-
- Stuart DD, Allen TM. A new liposomal formulation for antisense oligodeoxynucleotides with small size, high incorporation efficiency and good stability. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1463:219–229. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

