Correlation of ATP7B genotype with phenotype in Chinese patients with Wilson disease
- PMID: 14966923
- PMCID: PMC4716986
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i4.590
Correlation of ATP7B genotype with phenotype in Chinese patients with Wilson disease
Abstract
Aim: To determine the mutational characterization of P-type ATP7B gene and to explore the correlation of ATP7B genotype to phenotype in Chinese patients with Wilson disease (WD).
Methods: Seventy-five patients with WD from 72 no-kinship families, 44 males and 31 females, were enrolled in this study. The age of onset ranged from 4 to 39 years, <=18 years in 72 patients. Some exons of ATP7B gene mutations were analyzed in patients with WD by using biochemical methods, polymerase chain reaction-single strand configuration polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) and DNA sequence analysis. A total of 778 coding regions were identified with restriction enzyme Msp I. The activity of Cu-ATPase was assessed by measuring inorganic phosphorus.
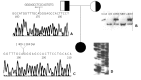
Results: Sixty-six of 75 patients (88%) had with hepatic manifestations, 39 of them had only hepatic manifestations, 27 patients had hepatic and neurological manifestations or other symptoms at the same time (16 patients had associated neurological manifestation, 3 patients had osteopathy, 8 patients had other symptoms). Eight of the 75 patients (10.7%) had only neurological symptoms, one patient (5 years old) had no symptom. Twelve changing patterns were detected in ATP7B gene by DNA sequencing, including seven mutations (R778L, C656X, G943D, V1140A, V1106I V1216M and 1384del17), six polymorphisms (IVS4-5t/c, A2495G, C2310G, IVS18+6c/t and IVS20+5a/g). R778L occurred in 49/66 patients (74%) with hepatic manifestations, homozygosis of R778L in 16 patients, heterozygosity of R778L in 33 patients. V1106I mutation of ATP7B gene occurred in 2 patients with delaying onset of clinical symptoms. Cu-ATPase activity of three patients with known mutations (R778L/V1106I/A2495G, R778L/V1216M and R778L/R778L) were determined, and the activity of Cu-ATPase was decreased by 44.55%, 88.23% and 69.49% respectively.
Conclusion: 1384del17bp is a novel mutation found in WD patients. R778L is the most common mutation of ATP7B gene. There is a correlation between R778L and hepatic manifestations in WD patient.
Figures

References
-
- Bull PC, Barwell JA, Hannah HT, Pautler SE, Higgins MJ, Lalande M, Cox DW. Isolation of new probes in the region of the Wilson disease locus, 13q14.2-->q14.3. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1993;64:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Thomas GR, Forbes JR, Roberts EA, Walshe JM, Cox DW. The Wilson disease gene: spectrum of mutations and their consequences. Nat Genet. 1995;9:210–217. - PubMed
-
- Shah AB, Chernov I, Zhang HT, Ross BM, Das K, Lutsenko S, Parano E, Pavone L, Evgrafov O, Ivanova-Smolenskaya IA, et al. Identification and analysis of mutations in the Wilson disease gene (ATP7B): population frequencies, genotype-phenotype correlation, and functional analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 1997;61:317–328. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu XQ, Zhang YF, Gu XF, Bao KR. Polymorphism analysis of ATP7B related microsatellite DNA haplotype in Wilson disease. Lab Medicine. 2002;(Suppl):S50–51.
-
- Gollan JL, Gollan TJ. Wilson disease in 1998: genetic, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. J Hepatol. 1998;28 Suppl 1:28–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

