Molecular insights into the interaction of PYM with the Mago-Y14 core of the exon junction complex
- PMID: 14968132
- PMCID: PMC1299003
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400091
Molecular insights into the interaction of PYM with the Mago-Y14 core of the exon junction complex
Abstract
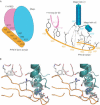
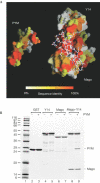
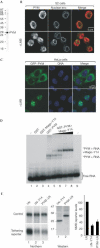
The exon junction complex (EJC) is deposited on mRNAs as a consequence of splicing and influences postsplicing mRNA metabolism. The Mago-Y14 heterodimer is a core component of the EJC. Recently, the protein PYM has been identified as an interacting partner of Mago-Y14. Here we show that PYM is a cytoplasmic RNA-binding protein that is excluded from the nucleus by Crm1. PYM interacts directly with Mago-Y14 by means of its N-terminal domain. The crystal structure of the Drosophila ternary complex at 1.9 A resolution reveals that PYM binds Mago and Y14 simultaneously, capping their heterodimerization interface at conserved surface residues. Formation of this ternary complex is also observed with the human proteins. Mago residues involved in the interaction with PYM have been implicated in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). Consistently, human PYM is active in NMD tethering assays. Together, these data suggest a role for PYM in NMD.
Figures


References
-
- Brünger AT et al. ( 1998) Crystallographic and NMR system: a new software system for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D 54: 905–921 - PubMed
-
- CCP4 ( 1994) The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D 50: 760–763 - PubMed
-
- Forler D, Kocher T, Rode M, Gentzel M, Izaurralde E, Wilm M ( 2003) An efficient protein complex purification method for functional proteomics in higher eukaryotes. Nat Biotech 21: 89–92 - PubMed
-
- Fribourg S, Gatfield D, Izaurralde E, Conti E ( 2003) A novel mode of RBD-protein recognition in the Y14–Mago complex. Nat Struct Biol 10: 433–439 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

