Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of 112 traditional Chinese medicinal plants associated with anticancer
- PMID: 14969719
- PMCID: PMC7126989
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2003.09.047
Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of 112 traditional Chinese medicinal plants associated with anticancer
Abstract
Cancer prevention and treatment using traditional Chinese medicines have attracted increasing interest. This study characterizes antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of traditional Chinese medicinal plants associated with anticancer, comprising 112 species from 50 plant families. The improved ABTS(*+) method was used to systematically assess the total antioxidant capacity (Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity, TEAC) of the medicinal extracts. The TEAC values and total phenolic content for methanolic extracts of herbs ranged from 46.7 to 17,323 micromol Trolox equivalent/100 g dry weight (DW), and from 0.22 to 50.3 g of gallic acid equivalent/100 g DW, respectively. A positive, significant linear relationship between antioxidant activity and total phenolic content (all R(2) values>/=0.95) showed that phenolic compounds were the dominant antioxidant components in the tested medicinal herbs. Major types of phenolic compounds from most of the tested herbs were preliminarily identified and analyzed, and mainly included phenolic acids, flavonoids, tannins, coumarins, lignans, quinones, stilbenes, and curcuminoids. These medicinal herbs exhibited far stronger antioxidant activity and contained significantly higher levels of phenolics than common vegetables and fruits. Traditional Chinese medicinal plants associated with anticancer might be potential sources of potent natural antioxidants and beneficial chemopreventive agents.
Figures
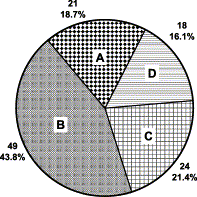


References
-
- Albanes D., Hartman T.J. Antioxidants and cancer: evidence from human observational studies and intervention trials. In: Papas A.M., editor. Antioxiant Status, Diet, Nutrition, and Health. CRC Press; Boca Raton, Florida: 1999. pp. 497–544.
-
- Andrade P.B., Seabra R.M., Valentão P., Areias F. Simultaneous determination of flavonoids, phenolic acids, and coumarins in seven medicinal species by HPLC/diode-array detector. Journal of Liquid Chromatography and Related Technologies. 1998;21(18):2813–2820.
-
- Aruoma O.I., Cuppett S.L. AOCS Press; Illinois: 1994. Antioxidant Methodology: In Vivo and In Vitro Concepts.
-
- Bo Q.M., Wu Z.Y., Shun Q.S., Bao X.S., Mao Z.S., Ha S.Q., Lu S.Y., Huang J.M. Shanghai Science and Technology Literature Press; Shanghai: 2002. A Selection of the Illustrated Chinese Anti-Cancer Herbal Medicines.
-
- Bouchet N., Lévesque J., Pousset J.L. HPLC isolation, identification and quantification of tannins from Guiera senegalensis. Phytochem Analysis. 2000;11(1):52–56.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

