Stent-coil treatment of a distal internal carotid artery dissecting pseudoaneurysm on a redundant loop by use of a flexible, dedicated nitinol intracranial stent
- PMID: 14970042
- PMCID: PMC7974624
Stent-coil treatment of a distal internal carotid artery dissecting pseudoaneurysm on a redundant loop by use of a flexible, dedicated nitinol intracranial stent
Abstract
Treatment of dissecting pseudoaneurysms of the distal cervical internal carotid artery with preservation of the parent artery by using stents or coils has become routine. Tortuosity remains a significant obstacle to successful endovascular treatment in some cases. We report the use of a stent-coil technique to treat a nonhealing dissecting pseudoaneurysm and associated stenosis with anatomic preservation of a redundant loop involving the stented arterial segment. This was accomplished by using a Neuroform dedicated intracranial stent.
Figures
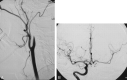

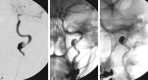
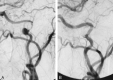
References
-
- Schievink WI, Wouter I. Current concepts: spontaneous dissection of the carotid and vertebral arteries. N Engl J Med 2001;344:898–906 - PubMed
-
- Guillon B, Brunerau L, Biousse V, et al. Long-term follow-up of aneurysms developed during extracranial internal carotid artery dissection. Neurology 1999;53:117–122 - PubMed
-
- Marks MP, Dake MD, Steinberg GK, et al. Stent placement for arterial and venous cerebrovascular disease: preliminary experience. Radiology 1994;191:441–446 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
