Dracunculiasis (guinea worm disease)
- PMID: 14970098
- PMCID: PMC332717
Dracunculiasis (guinea worm disease)
Abstract
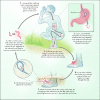
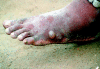
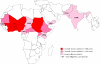
Dracunculiasis (guinea worm disease) is a parasitic disease that is limited to remote, rural villages in 13 sub-Saharan African countries that do not have access to safe drinking water. It is one the next diseases targeted for eradication by the World Health Organization. Guinea worm disease is transmitted by drinking water containing copepods (water fleas) that are infected with Dracunculiasis medinensis larvae. One year after human ingestion of infected water a female adult worm emerges, typically from a lower extremity, producing painful ulcers that can impair mobility for up to several weeks. This disease occurs annually when agricultural activities are at their peak. Large proportions of economically productive individuals of a village are usually affected simultaneously, resulting in decreased agricultural productivity and economic hardship. Eradication of guinea worm disease depends on prevention, as there is no effective treatment or vaccine. Since 1986, there has been a 98% reduction in guinea worm disease worldwide, achieved primarily through community-based programs. These programs have educated local populations on how to filter drinking water to remove the parasite and how to prevent those with ulcers from infecting drinking-water sources. Complete eradication will require sustained high-level political, financial and community support.
Figures



References
-
- Smith GS, Blum D, Huttley SRA, Okeke N, Kirkwood BR, Feachem RG. Disability from dracunculiasis: effect on mobility. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 1989;83(2):151-8. - PubMed
-
- Belcher DW, Wurapa FK, Ward WB, Lourie IM. Guinea worm in southern Ghana: its epidemiology and impact on agricultural productivity. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1975;24(2):243-9. - PubMed
-
- Watts SJ, Brieger WR, Yacoob M. Guinea worm: an in-depth study of what happens to mothers, families and communities. Soc Sci Med 1989;29(9):1043-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
