p38-MAPK signals survival by phosphorylation of caspase-8 and caspase-3 in human neutrophils
- PMID: 14970175
- PMCID: PMC2211830
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20031771
p38-MAPK signals survival by phosphorylation of caspase-8 and caspase-3 in human neutrophils
Abstract
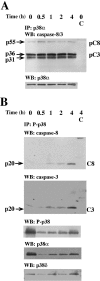
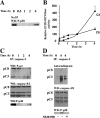
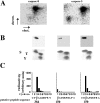
Neutrophil apoptosis occurs both in the bloodstream and in the tissue and is considered essential for the resolution of an inflammatory process. Here, we show that p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) associates to caspase-8 and caspase-3 during neutrophil apoptosis and that p38-MAPK activity, previously shown to be a survival signal in these primary cells, correlates with the levels of caspase-8 and caspase-3 phosphorylation. In in vitro experiments, immunoprecipitated active p38-MAPK phosphorylated and inhibited the activity of the active p20 subunits of caspase-8 and caspase-3. Phosphopeptide mapping revealed that these phosphorylations occurred on serine-364 and serine-150, respectively. Introduction of mutated (S150A), but not wild-type, TAT-tagged caspase-3 into primary neutrophils made the Fas-induced apoptotic response insensitive to p38-MAPK inhibition. Consequently, p38-MAPK can directly phosphorylate and inhibit the activities of caspase-8 and caspase-3 and thereby hinder neutrophil apoptosis, and, in so doing, regulate the inflammatory response.
Figures
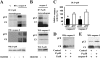
References
-
- Cartwright, G.E., G.W. Athens, and M.M. Wintrobe. 1964. The kinetics of granulopoiesis in normal man. Blood. 24:780–803. - PubMed
-
- Grigg, J.M., J.S. Savill, C. Sarraf, C. Haslett, and M. Silverman. 1991. Neutrophil apoptosis and clearance from neonatal lungs. Lancet. 338:720–722. - PubMed
-
- Cryns, V., and J. Yuan. 1998. Proteases to die for. Genes Dev. 12:1551–1570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

