Deficiency of the cyclin kinase inhibitor p21(WAF-1/CIP-1) promotes apoptosis of activated/memory T cells and inhibits spontaneous systemic autoimmunity
- PMID: 14970181
- PMCID: PMC2211831
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20031685
Deficiency of the cyclin kinase inhibitor p21(WAF-1/CIP-1) promotes apoptosis of activated/memory T cells and inhibits spontaneous systemic autoimmunity
Abstract
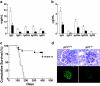
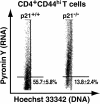
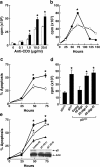
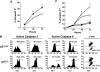
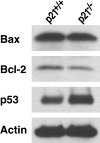
A characteristic feature of systemic lupus erythematosus is the accumulation of activated/memory T and B cells. These G0/G1-arrested cells express high levels of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors such as p21, are resistant to proliferation and apoptosis, and produce large amounts of proinflammatory cytokines. Herein, we show that ablation of p21 in lupus-prone mice allows these cells to reenter the cell cycle and undergo apoptosis, leading to autoimmune disease reduction. Absence of p21 resulted in enhanced Fas/FasL-mediated activation-induced T cell death, increased activation of procaspases 8 and 3, and loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential. Increased apoptosis was also associated with p53 up-regulation and a modest shift in the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 toward the proapoptotic Bax. Proliferation and apoptosis of B cells were also increased in p21-/- lupus mice. Thus, modulation of the cell cycle pathway may be a novel approach to reduce apoptosis-resistant pathogenic lymphocytes and to ameliorate systemic autoimmunity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
G1 arrest and high expression of cyclin kinase and apoptosis inhibitors in accumulated activated/memory phenotype CD4+ cells of older lupus mice.Eur J Immunol. 1997 Aug;27(8):1901-10. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270813. Eur J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9295025
-
p21CIP1/WAF1 controls proliferation of activated/memory T cells and affects homeostasis and memory T cell responses.J Immunol. 2007 Feb 15;178(4):2296-306. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.4.2296. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17277135
-
Role of cyclin kinase inhibitor p21 in systemic autoimmunity.J Immunol. 2001 Oct 1;167(7):4067-74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.7.4067. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11564828
-
Breakdown of self-tolerance and the pathogenesis of autoimmunity.Semin Nephrol. 1999 Jan;19(1):25-33. Semin Nephrol. 1999. PMID: 9952278 Review.
-
Theoretical and experimental approaches to generalized autoimmunity.Immunol Rev. 1990 Dec;118:129-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00815.x. Immunol Rev. 1990. PMID: 2079325 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Xenobiotic exposure and autoimmune hepatitis.Hepat Res Treat. 2010;2010:248157. doi: 10.1155/2010/248157. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Hepat Res Treat. 2010. PMID: 21253536 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinases: molecular switches controlling anergy and potential therapeutic targets for tolerance.Semin Immunol. 2007 Jun;19(3):173-9. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.02.009. Epub 2007 Mar 23. Semin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17383195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accelerated pathological and clinical nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus-prone New Zealand Mixed 2328 mice doubly deficient in TNF receptor 1 and TNF receptor 2 via a Th17-associated pathway.J Immunol. 2009 Feb 15;182(4):2532-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802948. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19201910 Free PMC article.
-
T-helper cell intrinsic defects in lupus that break peripheral tolerance to nuclear autoantigens.J Mol Med (Berl). 2005 Apr;83(4):267-78. doi: 10.1007/s00109-004-0624-2. Epub 2005 Jan 4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15630591 Review.
-
Differentially Expressed Gene Pathways in the Conjunctiva of Sjögren Syndrome Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 19;12:702755. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.702755. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34349764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sprent, J., and D.F. Tough. 1994. Lymphocyte life-span and memory. Science. 265:1395–1400. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed, R., and D. Gray. 1996. Immunological memory and protective immunity: understanding their relation. Science. 272:54–60. - PubMed
-
- Theofilopoulos, A.N., and D.H. Kono. 1999. Murine lupus models: gene-specific and genome-wide studies. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. R.G. Lahita, editor. Academic Press, San Diego. 145–181.
-
- Chu, E.B., D.N. Ernst, M.V. Hobbs, and W.O. Weigle. 1994. Maturational changes in CD4+ cell subsets and lymphokine production in BXSB mice. J. Immunol. 152:4129–4138. - PubMed
-
- Sabzevari, H., S. Propp, D.H. Kono, and A.N. Theofilopoulos. 1997. G1 arrest and high expression of cyclin kinase and apoptosis inhibitors in accumulated activated/memory phenotype CD4+ cells of older lupus mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 27:1901–1910. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

