Mutagenesis of the putative sterol-sensing domain of yeast Niemann Pick C-related protein reveals a primordial role in subcellular sphingolipid distribution
- PMID: 14970192
- PMCID: PMC2171978
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200310046
Mutagenesis of the putative sterol-sensing domain of yeast Niemann Pick C-related protein reveals a primordial role in subcellular sphingolipid distribution
Abstract
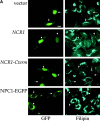
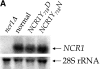
Lipid movement between organelles is a critical component of eukaryotic membrane homeostasis. Niemann Pick type C (NP-C) disease is a fatal neurodegenerative disorder typified by lysosomal accumulation of cholesterol and sphingolipids. Expression of yeast NP-C-related gene 1 (NCR1), the orthologue of the human NP-C gene 1 (NPC1) defective in the disease, in Chinese hamster ovary NPC1 mutant cells suppressed lipid accumulation. Deletion of NCR1, encoding a transmembrane glycoprotein predominantly residing in the vacuole of normal yeast, gave no phenotype. However, a dominant mutation in the putative sterol-sensing domain of Ncr1p conferred temperature and polyene antibiotic sensitivity without changes in sterol metabolism. Instead, the mutant cells were resistant to inhibitors of sphingolipid biosynthesis and super sensitive to sphingosine and C2-ceramide. Moreover, plasma membrane sphingolipids accumulated and redistributed to the vacuole and other subcellular membranes of the mutant cells. We propose that the primordial function of these proteins is to recycle sphingolipids and that defects in this process in higher eukaryotes secondarily result in cholesterol accumulation.
Copyright The Rockefeller University Press
Figures












Similar articles
-
The sterol-sensing domain of the Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) protein regulates trafficking of low density lipoprotein cholesterol.J Biol Chem. 2005 Aug 5;280(31):28581-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M414024200. Epub 2005 May 20. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15908696
-
A yeast model system for functional analysis of the Niemann-Pick type C protein 1 homolog, Ncr1p.Traffic. 2005 Oct;6(10):907-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00327.x. Traffic. 2005. PMID: 16138904
-
Identification and characterization of protein interactions with the major Niemann-Pick type C disease protein in yeast reveals pathways of therapeutic potential.Genetics. 2023 Aug 31;225(1):iyad129. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad129. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 37440478 Free PMC article.
-
Sterol uptake by the NPC system in eukaryotes: a Saccharomyces cerevisiae perspective.FEBS Lett. 2022 Jan;596(2):160-179. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14253. Epub 2021 Dec 20. FEBS Lett. 2022. PMID: 34897668 Review.
-
Niemann-Pick type C mutations cause lipid traffic jam.Traffic. 2000 Mar;1(3):218-25. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010304.x. Traffic. 2000. PMID: 11208105 Review.
Cited by
-
Candida albicans phospholipomannan: a sweet spot for controlling host response/inflammation.Semin Immunopathol. 2015 Mar;37(2):123-30. doi: 10.1007/s00281-014-0461-5. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Semin Immunopathol. 2015. PMID: 25394861 Review.
-
The 'permeome' of the malaria parasite: an overview of the membrane transport proteins of Plasmodium falciparum.Genome Biol. 2005;6(3):R26. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-3-r26. Epub 2005 Mar 2. Genome Biol. 2005. PMID: 15774027 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Contact Sites in Yeast: Control Hubs of Sphingolipid Homeostasis.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Dec 9;11(12):971. doi: 10.3390/membranes11120971. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34940472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expanding boundaries of sphingolipid lysosomal storage diseases; insights from Niemann-Pick disease type C.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Oct 31;51(5):1777-1787. doi: 10.1042/BST20220711. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 37844193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasmodium Niemann-Pick type C1-related protein is a druggable target required for parasite membrane homeostasis.Elife. 2019 Mar 19;8:e40529. doi: 10.7554/eLife.40529. Elife. 2019. PMID: 30888318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel, F.M., R. Brent, R.E. Kingston, D.D. Moore, J.G. Seidman, J.A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1998. Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York. 13.0.1–13.13.9.
-
- Bergstrom, J.D., M.M. Kurtz, D.J. Rew, A.M. Amend, J.D. Karkas, R.G. Bostedor, V.S. Bansal, C. Dufresne, F.L. VanMiddlesworth, O.D. Hensens, et al. 1993. Zaragozic acids: a family of fungal metabolites that are picomolar competitive inhibitors of squalene synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 90:80–84. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carstea, E.D., J.A. Morris, K.G. Coleman, S.K. Loftus, D. Zhang, C. Cummings, J. Gu, M.A. Rosenfeld, W.J. Pavan, D.B. Krizman, et al. 1997. Niemann-Pick C1 disease gene: homology to mediators of cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 277:228–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

