miRNP:mRNA association in polyribosomes in a human neuronal cell line
- PMID: 14970384
- PMCID: PMC1370934
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.5181104
miRNP:mRNA association in polyribosomes in a human neuronal cell line
Abstract
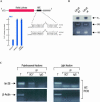
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small regulatory RNAs that control gene expression by base-pairing with their mRNA targets. miRNAs assemble into ribonucleoprotein complexes termed miRNPs. Animal miRNAs recognize their mRNA targets via partial antisense complementarity and repress mRNA translation at a step after translation initiation. How animal miRNAs recognize their mRNA targets and how they control their translation is unknown. Here we describe that in a human neuronal cell line, the miRNP proteins eIF2C2 (a member of the Argonaute family of proteins), Gemin3, and Gemin4 along with miRNAs cosediment with polyribosomes. Furthermore, we describe a physical association between a let-7b (miRNA)-containing miRNP and its putative human mRNA target in polyribosome-containing fractions. These findings suggest that miRNP proteins may play important roles in target mRNA recognition and translational repression.
Figures



References
-
- Ambros, V. 2000. Control of developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 10: 428–433. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, E., Caudy, A.A., Hammond, S.M., and Hannon, G.J. 2001. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409: 363–366. - PubMed
-
- Carmell, M.A., Xuan, Z., Zhang, M.Q., and Hannon, G.J. 2002. The Argonaute family: Tentacles that reach into RNAi, developmental control, stem cell maintenance, and tumorigenesis. Genes & Dev. 16: 2733–2742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
