Sequence-specific inhibition of microRNA- and siRNA-induced RNA silencing
- PMID: 14970398
- PMCID: PMC1370948
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.5235104
Sequence-specific inhibition of microRNA- and siRNA-induced RNA silencing
Abstract
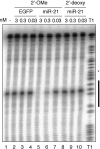
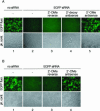
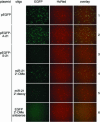
A large number of miRNAs have recently been discovered in plants and animals. Development of reverse genetic approaches that act to inhibit microRNA function would facilitate the study of this new class of noncoding RNA. Here we show that 2'-O-methyl oligoribonucleotides, but not 2'-deoxyoligonucleotides specifically inactivate the RNAi activity associated with miRNA-protein complexes in human cell extracts as well as in cultured human cells.
Figures
References
-
- Abrahante, J.E., Daul, A.L., Li, M., Volk, M.L., Tennessen, J.M., Miller, E.A., and Rougvie, A.E. 2003. The Caenorhabditis elegans hunchback-like gene lin-57/hbl-1 controls developmental time and is regulated by microRNAs. Dev. Cell 4: 625–637. - PubMed
-
- Ambros, V. 2003. MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: Growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 113: 673–676. - PubMed
-
- Ambros, V., Lee, R.C., Lavanway, A., Williams, P.T., and Jewell, D. 2003. MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 13: 807–818. - PubMed
-
- Aravin, A.A., Lagos-Quintana, M., Yalcin, A., Zavolan, M., Marks, D., Snyder, B., Gaasterland, T., Meyer, J., and Tuschl, T. 2003. The small RNA profile during Drosophila melanogaster development. Dev. Cell 5: 337–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
