Studies of the interaction of Escherichia coli YjeQ with the ribosome in vitro
- PMID: 14973029
- PMCID: PMC344419
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.5.1381-1387.2004
Studies of the interaction of Escherichia coli YjeQ with the ribosome in vitro
Abstract
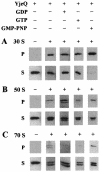
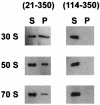
Escherichia coli YjeQ represents a conserved group of bacteria-specific nucleotide-binding proteins of unknown physiological function that have been shown to be essential to the growth of E. coli and Bacillus subtilis. The protein has previously been characterized as possessing a slow steady-state GTP hydrolysis activity (8 h(-1)) (D. M. Daigle, L. Rossi, A. M. Berghuis, L. Aravind, E. V. Koonin, and E. D. Brown, Biochemistry 41: 11109-11117, 2002). In the work reported here, YjeQ from E. coli was found to copurify with ribosomes from cell extracts. The copy number of the protein per cell was nevertheless low relative to the number of ribosomes (ratio of YjeQ copies to ribosomes, 1:200). In vitro, recombinant YjeQ protein interacted strongly with the 30S ribosomal subunit, and the stringency of that interaction, revealed with salt washes, was highest in the presence of the nonhydrolyzable GTP analog 5'-guanylylimidodiphosphate (GMP-PNP). Likewise, association with the 30S subunit resulted in a 160-fold stimulation of YjeQ GTPase activity, which reached a maximum with stoichiometric amounts of ribosomes. N-terminal truncation variants of YjeQ revealed that the predicted OB-fold region was essential for ribosome binding and GTPase stimulation, and they showed that an N-terminal peptide (amino acids 1 to 20 in YjeQ) was necessary for the GMP-PNP-dependent interaction of YjeQ with the 30S subunit. Taken together, these data indicate that the YjeQ protein participates in a guanine nucleotide-dependent interaction with the ribosome and implicate this conserved, essential GTPase as a novel factor in ribosome function.
Figures





References
-
- An, G., B. R. Glick, J. D. Friesen, and M. C. Ganoza. 1980. Identification and quantitation of elongation factor EF-P in Escherichia coli cell-free extracts. Can. J. Biochem. 97:23-28. - PubMed
-
- Aoki, H., K. Dekany, S.-L. Adams, and M. C. Ganoza. 1997. The gene encoding the elongation factor P protein is essential for viability and is required for protein synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 272:32254-32259. - PubMed
-
- Arcus, V. 2002. OB-fold domains: a snapshot of the evolution of sequence, structure and function. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12:794-801. - PubMed
-
- Arigoni, F., F. Talabot, M. Peitsch, M. D. Edgerton, E. Meldrum, E. Allet, R. Fish, T. Jamotte, M. L. Curchod, and H. Loferer. 1998. A genome-based approach for the identification of essential bacterial genes. Nat. Biotechnol. 16:851-856. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1994. Current protocols in molecular biology, vol. 2, chapter 11, section 11.12-11.13. John Wiley & Sons Inc., Boston, Mass.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

