Functionally critical elements of CooA-related CO sensors
- PMID: 14973040
- PMCID: PMC344431
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.5.1320-1329.2004
Functionally critical elements of CooA-related CO sensors
Abstract
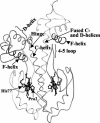
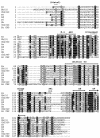
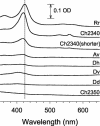
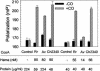
CooA is a heme-containing transcriptional activator that enables Rhodospirillum rubrum to sense and grow on CO as a sole energy source. We have identified a number of CooA homologs through database searches, expressed these heterologously in Escherichia coli, and monitored their ability to respond to CO in vivo. Further in vitro analysis of two CooA homologs from Azotobacter vinelandii and Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans corroborated the in vivo data by revealing the ability of CO to bind to these hemoproteins and stimulate their binding at specific DNA sequences. These data, as well as the patterns of conserved residues in the homologs, are compared to what is already known about functionally important residues in the CooA protein of R. rubrum. The results identify critical regions of CooA and indicate features that distinguish CooAs from the general family of cyclic AMP receptor proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Aono, S., K. Ohkubo, T. Matsuo, and H. Nakajima. 1998. Redox-controlled ligand exchange of the heme in the CO-sensing transcriptional activator CooA. J. Biol. Chem. 273:25757-25764. - PubMed
-
- Boehning, D., and S. H. Snyder. 2003. Novel neural modulators. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 26:105-131. - PubMed
-
- Coyle, C. M., M. Puranik, H. Youn, S. B. Nielsen, R. D. Williams, R. L. Kerby, G. P. Roberts, and T. G. Spiro. 2003. Activation mechanism of the CO sensor CooA: mutational and resonance Raman spectroscopic studies. J. Biol. Chem. 278:35384-35393. - PubMed
-
- Dobbek, H., V. Svetlitchnyi, L. Gremer, R. Huber, and O. Meyer. 2001. Crystal structure of a carbon monoxide dehydrogenase reveals a [Ni-4Fe-5S] cluster. Science 293:1281-1285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

