The Melampsora lini AvrL567 avirulence genes are expressed in haustoria and their products are recognized inside plant cells
- PMID: 14973158
- PMCID: PMC385286
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.020040
The Melampsora lini AvrL567 avirulence genes are expressed in haustoria and their products are recognized inside plant cells
Abstract
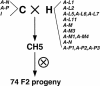
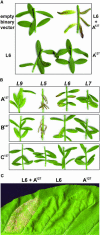
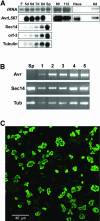
The Linum usitatissimum (flax) L gene alleles, which encode nucleotide binding site-Leu rich repeat class intracellular receptor proteins, confer resistance against the Melampsora lini (flax rust) fungus. At least 11 different L resistance specificities are known, and the corresponding avirulence genes in M. lini map to eight independent loci, some of which are complex and encode multiple specificities. We identified an M. lini cDNA marker that cosegregates in an F2 rust family with a complex locus determining avirulence on the L5, L6, and L7 resistance genes. Two related avirulence gene candidates, designated AvrL567-A and AvrL567-B, were identified in a genomic DNA contig from the avirulence allele, whereas the corresponding virulence allele contained a single copy of a related gene, AvrL567-C. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transient expression of the mature AvrL567-A or AvrL567-B (but not AvrL567-C) proteins as intracellular products in L. usitatissimum and Nicotiana tabacum (tobacco) induced a hypersensitive response-like necrosis that was dependent on coexpression of the L5, L6, or L7 resistance gene. An F1 seedling lethal or stunted growth phenotype also was observed when transgenic L. usitatissimum plants expressing AvrL567-A or AvrL567-B (but not AvrL567-C) were crossed to resistant lines containing L5, L6, or L7. The AvrL567 genes are expressed in rust haustoria and encode 127 amino acid secreted proteins. Intracellular recognition of these rust avirulence proteins implies that they are delivered into host cells across the plant membrane. Differences in the three AvrL567 protein sequences result from diversifying selection, which is consistent with a coevolutionary arms race.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Crystal structures of flax rust avirulence proteins AvrL567-A and -D reveal details of the structural basis for flax disease resistance specificity.Plant Cell. 2007 Sep;19(9):2898-912. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.053611. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 17873095 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation of the flax rust fungus, Melampsora lini: selection via silencing of an avirulence gene.Plant J. 2010 Jan;61(2):364-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04052.x. Epub 2009 Oct 26. Plant J. 2010. PMID: 19874543 Free PMC article.
-
Haustorially expressed secreted proteins from flax rust are highly enriched for avirulence elicitors.Plant Cell. 2006 Jan;18(1):243-56. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.035980. Epub 2005 Dec 2. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 16326930 Free PMC article.
-
Flax rust resistance gene specificity is based on direct resistance-avirulence protein interactions.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2007;45:289-306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.45.062806.094331. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2007. PMID: 17430087 Review.
-
Avirulence proteins from haustoria-forming pathogens.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 Apr;269(2):181-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00684.x. Epub 2007 Mar 2. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17343675 Review.
Cited by
-
A viral resistance gene from common bean functions across plant families and is up-regulated in a non-virus-specific manner.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 8;103(32):11856-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604815103. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16880399 Free PMC article.
-
Endocytosis in plant-microbe interactions.Protoplasma. 2010 Dec;247(3-4):177-93. doi: 10.1007/s00709-010-0195-8. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Protoplasma. 2010. PMID: 20814704 Review.
-
Interaction of a Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei effector candidate with a barley ARF-GAP suggests that host vesicle trafficking is a fungal pathogenicity target.Mol Plant Pathol. 2014 Aug;15(6):535-49. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12110. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Mol Plant Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24304971 Free PMC article.
-
Changing the Game: Using Integrative Genomics to Probe Virulence Mechanisms of the Stem Rust Pathogen Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Feb 24;7:205. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00205. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 26941766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Puccinia coronata f. sp. avenae: a threat to global oat production.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 May;19(5):1047-1060. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12608. Epub 2017 Dec 10. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 28846186 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Axtell, M.J., Chisholm, S.T., Dahlbeck, D., and Staskawicz, B.J. (2003). Genetic and molecular evidence that the Pseudomonas syringae type III effector protein AvrRpt2 is a cysteine protease. Mol. Microbiol. 49, 1537–1546. - PubMed
-
- Axtell, M.J., and Staskawicz, B.J. (2003). Initiation of RPS2-specified disease resistance is coupled to AvrRpt2-directed elimination of RIN4. Cell 112, 369–377. - PubMed
-
- Ayliffe, M.A., Dodds, P.N., and Lawrence, G.J. (2001). Characterisation of the beta-tubulin genes from Melampsora lini and comparison of fungal beta-tubulin genes. Mycol. Res. 105, 818–826.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

