Protein phosphorylation in amyloplasts regulates starch branching enzyme activity and protein-protein interactions
- PMID: 14973170
- PMCID: PMC385281
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.017400
Protein phosphorylation in amyloplasts regulates starch branching enzyme activity and protein-protein interactions
Abstract
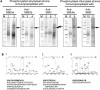
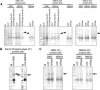
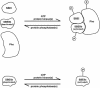
Protein phosphorylation in amyloplasts and chloroplasts of Triticum aestivum (wheat) was investigated after the incubation of intact plastids with gamma-(32)P-ATP. Among the soluble phosphoproteins detected in plastids, three forms of starch branching enzyme (SBE) were phosphorylated in amyloplasts (SBEI, SBEIIa, and SBEIIb), and both forms of SBE in chloroplasts (SBEI and SBEIIa) were shown to be phosphorylated after sequencing of the immunoprecipitated (32)P-labeled phosphoproteins using quadrupole-orthogonal acceleration time of flight mass spectrometry. Phosphoamino acid analysis of the phosphorylated SBE forms indicated that the proteins are all phosphorylated on Ser residues. Analysis of starch granule-associated phosphoproteins after incubation of intact amyloplasts with gamma-(32)P-ATP indicated that the granule-associated forms of SBEII and two granule-associated forms of starch synthase (SS) are phosphorylated, including SSIIa. Measurement of SBE activity in amyloplasts and chloroplasts showed that phosphorylation activated SBEIIa (and SBEIIb in amyloplasts), whereas dephosphorylation using alkaline phosphatase reduced the catalytic activity of both enzymes. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation had no effect on the measurable activity of SBEI in amyloplasts and chloroplasts, and the activities of both granule-bound forms of SBEII in amyloplasts were unaffected by dephosphorylation. Immunoprecipitation experiments using peptide-specific anti-SBE antibodies showed that SBEIIb and starch phosphorylase each coimmunoprecipitated with SBEI in a phosphorylation-dependent manner, suggesting that these enzymes may form protein complexes within the amyloplast in vivo. Conversely, dephosphorylation of immunoprecipitated protein complex led to its disassembly. This article reports direct evidence that enzymes of starch metabolism (amylopectin synthesis) are regulated by protein phosphorylation and indicate a wider role for protein phosphorylation and protein-protein interactions in the control of starch anabolism and catabolism.
Figures



References
-
- Ball, S., Guan, H.-P., James, M., Myers, A., Keeling, P., Mouille, G., Buléon, A., Colonna, P., and Preiss, J. (1996). From glycogen to amylopectin: A model for the biogenesis of the plant starch granule. Cell 86, 349–352. - PubMed
-
- Ball, S.G., and Morell, M.K. (2003). From bacterial glycogen to starch: Understanding the biogenesis of the plant starch granule. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 54, 207–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

