Surfection: a new platform for transfected cell arrays
- PMID: 14973329
- PMCID: PMC373424
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gnh029
Surfection: a new platform for transfected cell arrays
Abstract
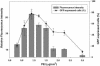
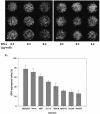
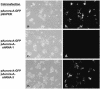
Efficient high-throughput expression of genes in mammalian cells can facilitate large-scale functional genomic studies. Towards this aim, we developed a simple yet powerful method to deliver genes into cells by cationic polymers on the surface of substrates. Transfection can be achieved by directly contacting nucleic acid-cell mixtures with the cationic substrates, e.g. polyethylenimine/collagen-coated wells. This single-step matrix-surface- mediated transfection method, termed 'surfection', can efficiently deliver multiple plasmids into cells and can successfully assay siRNA-mediated gene silencing. This technology represents the easiest method to transfer combinations of genes in large-scale arrays, and is a versatile tool for live-cell imaging and cell-based drug screening.
Figures



References
-
- Shea L.D., Smiley,E., Bonadio,J. and Mooney,D.J. (1999) DNA delivery from polymer matrices for tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol., 17, 551–554. - PubMed
-
- Klugherz B.D., Jones,P.L., Cui,X., Chen,W., Meneveau,N.F., DeFelice,S., Connolly,J., Wilensky,R.L. and Levy,R.J. (2000) Gene delivery from a DNA controlled-release stent in porcine coronary arteries. Nat. Biotechnol., 18, 1181–1184. - PubMed
-
- Honma K., Ochiya,T., Nagahara,S., Sano,A., Yamamoto,H., Hirai,K., Aso,Y. and Terada,M. (2001) Atelocollagen-based gene transfer in cells allows high-throughput screening of gene functions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 289, 1075–1081. - PubMed
-
- Perlstein I., Connolly,J.M., Cui,X., Song,C., Li,Q., Jones,P.L., Lu,Z., DeFelice,S., Klugherz,B., Wilensky,R. et al. (2003) DNA delivery from an intravascular stent with a denatured collagen-polylactic-polyglycolic acid-controlled release coating: mechanisms of enhanced transfection. Gene Ther., 10, 1420–1428. - PubMed
-
- Jang J.H. and Shea,L.D. (2003) Controllable delivery of non-viral DNA from porous scaffolds. J. Control. Release, 86, 157–168. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

