Unlocking hidden genomic sequence
- PMID: 14973330
- PMCID: PMC373418
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gnh022
Unlocking hidden genomic sequence
Abstract
Despite the success of conventional Sanger sequencing, significant regions of many genomes still present major obstacles to sequencing. Here we propose a novel approach with the potential to alleviate a wide range of sequencing difficulties. The technique involves extracting target DNA sequence from variants generated by introduction of random mutations. The introduction of mutations does not destroy original sequence information, but distributes it amongst multiple variants. Some of these variants lack problematic features of the target and are more amenable to conventional sequencing. The technique has been successfully demonstrated with mutation levels up to an average 18% base substitution and has been used to read previously intractable poly(A), AT-rich and GC-rich motifs.
Figures
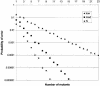

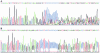





Similar articles
-
Algorithms for sequence analysis via mutagenesis.Bioinformatics. 2004 Oct 12;20(15):2401-10. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth258. Epub 2004 May 14. Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15145816
-
Reliable handling of highly A/T-rich genomic DNA for efficient generation of knockin strains of Dictyostelium discoideum.BMC Biotechnol. 2016 Apr 14;16:37. doi: 10.1186/s12896-016-0267-8. BMC Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27075750 Free PMC article.
-
Poly: a quantitative analysis tool for simple sequence repeat (SSR) tracts in DNA.BMC Bioinformatics. 2003 Jun 5;4:22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-4-22. Epub 2003 Jun 5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 12791171 Free PMC article.
-
A frequency-controlled random mutagenesis method for GC-rich genes.Anal Biochem. 2009 May 15;388(2):356-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2009.02.036. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Anal Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19268416
-
Variations in mitochondrial tRNA(Thr) gene may not be associated with coronary heart disease.Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal. 2016;27(1):565-8. doi: 10.3109/19401736.2014.905862. Epub 2014 Apr 8. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal. 2016. PMID: 24708135
Cited by
-
Trial and error: how the unclonable human mitochondrial genome was cloned in yeast.Pharm Res. 2011 Nov;28(11):2863-70. doi: 10.1007/s11095-011-0527-1. Epub 2011 Jul 9. Pharm Res. 2011. PMID: 21739320
-
Mastering DNA chromatogram analysis in Sanger sequencing for reliable clinical analysis.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2023 Nov 13;21(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s43141-023-00587-6. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37955813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An intermediate grade of finished genomic sequence suitable for comparative analyses.Genome Res. 2004 Nov;14(11):2235-44. doi: 10.1101/gr.2648404. Epub 2004 Oct 12. Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15479945 Free PMC article.
-
An improved protocol for sequencing of repetitive genomic regions and structural variations using mutagenesis and next generation sequencing.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043359. Epub 2012 Aug 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22912860 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing and measuring bias in sequence data.Genome Biol. 2013 May 29;14(5):R51. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-5-r51. Genome Biol. 2013. PMID: 23718773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lander E.S., Linton,L.M., Birren,B., Nusbaum,C., Zody,M.C., Baldwin,J., Devon,K., Dewar,K., Doyle,M., FitzHugh,W. et al. The International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature, 409, 860–921. - PubMed
-
- Glöckner G., Eichinger,L., Szafranski,K., Pachebat,J.A., Bankier,A.T., Dear,P.H., Lehmann,R., Baumgart,C., Parra,G., Abril,J.F. et al. (2002) Sequence and analysis of chromosome 2 of Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature, 418, 79–85. - PubMed
-
- Donlin M.J. and Johnson,K.A. (1994) Mutants affecting nucleotide recognition by T7 DNA polymerase. Biochemistry, 33, 14908–14917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

