Deficiency of GDP-Man:GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol mannosyltransferase causes congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ik
- PMID: 14973778
- PMCID: PMC1182261
- DOI: 10.1086/382492
Deficiency of GDP-Man:GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol mannosyltransferase causes congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ik
Abstract
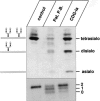
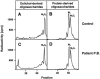
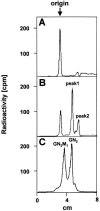
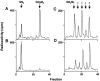
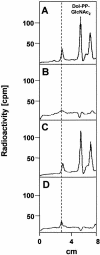
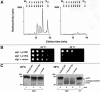
The molecular nature of a severe multisystemic disorder with a recurrent nonimmune hydrops fetalis was identified as deficiency of GDP-Man:GlcNAc(2)-PP-dolichol mannosyltransferase, the human orthologue of the yeast ALG1 gene (MIM 605907). The disease belongs to the group of congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG) and is designated as subtype CDG-Ik. In patient-derived serum, the total amount of the glycoprotein transferrin was reduced. Moreover, a partial loss of N-glycan chains was observed, a characteristic feature of CDG type I forms. Metabolic labeling with [6-(3)H]glucosamine revealed an accumulation of GlcNAc(2)-PP-dolichol and GlcNAc(1)-PP-dolichol in skin fibroblasts of the patient. Incubation of fibroblast extracts with [(14)C]GlcNAc(2)-PP-dolichol and GDP-mannose indicated a severely reduced activity of the beta 1,4-mannosyltransferase, elongating GlcNAc(2)-PP-dolichol to Man(1)GlcNAc(2)-PP-dolichol at the cytosolic side of the endoplasmic reticulum. Genetic analysis of the patient's hALG1 gene identified a homozygous mutation leading to the exchange of a serine residue to leucine at position 258 in the hALG1 protein. The disease-causing nature of the hALG1 mutation for the glycosylation defect was verified by a retroviral complementation approach in patient-derived primary fibroblasts and was confirmed by the expression of wild-type and mutant hALG1 in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae alg1-1 strain.
Figures
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Entrez Database, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Entrez/ (for hALG1 cDNA [accession number BAA90748])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for ALG1 and CDG-Ii)
References
-
- Aebi M, Helenius A, Schenk B, Barone R, Fiumara A, Berger EG, Hennet T, et al (1999) Carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndromes become congenital disorders of glycosylation: an updated nomenclature for CDG. First International Workshop on CDGS. Glycoconj J 16:669–67110.1023/A:1017249723165 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gietz RD, Schiestl RH (1991) Applications of high efficiency lithium acetate transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as carrier. Yeast 7:253–263 - PubMed
-
- Huffaker T, Robbins P (1982) Temperature-sensitive yeast mutants deficient in asparagine-linked glycosylation. J Biol Chem 257:3203–3210 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

