Offset of pharmacodynamic effects and safety of remifentanil in intensive care unit patients with various degrees of renal impairment
- PMID: 14975051
- PMCID: PMC420060
- DOI: 10.1186/cc2399
Offset of pharmacodynamic effects and safety of remifentanil in intensive care unit patients with various degrees of renal impairment
Abstract
Introduction: This open label, multicentre study was conducted to assess the times to offset of the pharmacodynamic effects and the safety of remifentanil in patients with varying degrees of renal impairment requiring intensive care.
Methods: A total of 40 patients, who were aged 18 years or older and had normal/mildly impaired renal function (estimated creatinine clearance >/= 50 ml/min; n = 10) or moderate/severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance <50 ml/min; n = 30), were entered into the study. Remifentanil was infused for up to 72 hours (initial rate 6-9 microgram/kg per hour), with propofol administered if required, to achieve a target Sedation-Agitation Scale score of 2-4, with no or mild pain.
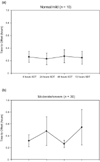
Results: There was no evidence of increased offset time with increased duration of exposure to remifentanil in either group. The time to offset of the effects of remifentanil (at 8, 24, 48 and 72 hours during scheduled down-titrations of the infusion) were more variable and were statistically significantly longer in the moderate/severe group than in the normal/mild group at 24 hours and 72 hours. These observed differences were not clinically significant (the difference in mean offset at 72 hours was only 16.5 min). Propofol consumption was lower with the remifentanil based technique than with hypnotic based sedative techniques. There were no statistically significant differences between the renal function groups in the incidence of adverse events, and no deaths were attributable to remifentanil use.
Conclusion: Remifentanil was well tolerated, and the offset of pharmacodynamic effects was not prolonged either as a result of renal dysfunction or prolonged infusion up to 72 hours.
Figures
Comment in
-
Remifentanil for analgesia-based sedation in the intensive care unit.Crit Care. 2004 Feb;8(1):13-4. doi: 10.1186/cc2421. Epub 2003 Dec 17. Crit Care. 2004. PMID: 14975040 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Decreased duration of mechanical ventilation when comparing analgesia-based sedation using remifentanil with standard hypnotic-based sedation for up to 10 days in intensive care unit patients: a randomised trial [ISRCTN47583497].Crit Care. 2005 Jun;9(3):R200-10. doi: 10.1186/cc3495. Epub 2005 Mar 15. Crit Care. 2005. PMID: 15987391 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of analgesia-based sedation with remifentanil versus standard hypnotic-based regimens in intensive care unit patients with brain injuries: a randomised, controlled trial [ISRCTN50308308].Crit Care. 2004 Aug;8(4):R268-80. doi: 10.1186/cc2896. Epub 2004 Jun 28. Crit Care. 2004. PMID: 15312228 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Remifentanil versus fentanyl for analgesia based sedation to provide patient comfort in the intensive care unit: a randomized, double-blind controlled trial [ISRCTN43755713].Crit Care. 2004 Feb;8(1):R1-R11. doi: 10.1186/cc2398. Epub 2003 Nov 20. Crit Care. 2004. PMID: 14975049 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Analgosedation: a paradigm shift in intensive care unit sedation practice.Ann Pharmacother. 2012 Apr;46(4):530-40. doi: 10.1345/aph.1Q525. Epub 2012 Apr 10. Ann Pharmacother. 2012. PMID: 22496477 Review.
-
Remifentanil in critically ill cardiac patients.Ann Card Anaesth. 2011 Jan-Apr;14(1):6-12. doi: 10.4103/0971-9784.74393. Ann Card Anaesth. 2011. PMID: 21196668 Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased duration of mechanical ventilation when comparing analgesia-based sedation using remifentanil with standard hypnotic-based sedation for up to 10 days in intensive care unit patients: a randomised trial [ISRCTN47583497].Crit Care. 2005 Jun;9(3):R200-10. doi: 10.1186/cc3495. Epub 2005 Mar 15. Crit Care. 2005. PMID: 15987391 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adjunctive remifentanil infusion in deeply sedated and paralyzed ICU patients during fiberoptic bronchoscopy procedure: a prospective, randomized, controlled study.Ann Intensive Care. 2012 Jul 16;2(1):29. doi: 10.1186/2110-5820-2-29. Ann Intensive Care. 2012. PMID: 22800647 Free PMC article.
-
Could remifentanil reduce duration of mechanical ventilation in comparison with other opioids for mechanically ventilated patients? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2017 Aug 3;21(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1789-8. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28774327 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Fentanyl, Sufentanil, and Remifentanil With Length of Stay and Mortality Among Mechanically Ventilated Patients: A Registry-Based Cohort Study.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 4;13:858531. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.858531. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35308226 Free PMC article.
-
Remifentanil vs. dexmedetomidine for cardiac surgery patients with noninvasive ventilation intolerance: a multicenter randomized controlled trial.J Intensive Care. 2024 Sep 18;12(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40560-024-00750-2. J Intensive Care. 2024. PMID: 39294818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Westmoreland CL, Hoke JF, Sebel PS, Hug CC, Jr, Muir KT. Pharmacokinetics of remifentanil (GI87084B) and its major metabolite (GR90291) in patients undergoing elective surgery. Anesthesiology. 1993;79:893–903. - PubMed
-
- Park GR, Evans TN. Remifentanil in the critically ill: what will its place be? Br J Intensive Care. 1996;79:893–903.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

