Age-stratified QTL genome scan analyses for anthropometric measures
- PMID: 14975099
- PMCID: PMC1866467
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-4-S1-S31
Age-stratified QTL genome scan analyses for anthropometric measures
Abstract
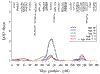
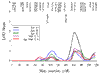
With the availability of longitudinal data, age-specific (stratified) or age-adjusted genetic analyses have the potential to localize different putative trait influencing loci. If age does not influence the locus-specific penetrance function within the range examined, age-stratified analyses will tend to yield comparable results for an individual trait. However, age-stratified results should vary across age strata when the locus-specific penetrance function is age dependent. In this paper, age-stratified and age-adjusted quantitative trait loci (QTL) linkage analyses were contrasted for height, weight, body mass index (BMI), and systolic blood pressure on a subset of the Framingham Heart Study. The strata comprised individuals with data present in each of three age groups: 31-49, 50-60, 61-79. Genome-wide QTL analyses were performed using SOLAR. Over all ages, a linkage signal for height was detected on chromosome 14q11.2 near marker GATA74E02A (LOD for ages 31-49 = 2.38, LOD for ages 50-60 = 1.84, LOD for ages 61-79 = 2.45). Evidence of linkage to BMI in the 31-49 age group was found on chromosome 3q22 (GATA3C02, LOD = 2.89, p = 0.0003) at the same location as the signal for weight (LOD = 3.10, p = 0.0002). Linkage was also supported on chromosome 1p22.1 for BMI (LOD = 2.21, p = 0.0014) and weight (LOD = 2.47, p = 0.0007) in the 31-49 age group. Our age-stratified results suggest that QTL that are expressed over long periods of time and affecting multiple, correlated traits may be identified using genome scan and variance-component methodology to help detect early and/or late gene expression.
Figures
References
-
- Franklin S, Larson M, Khan S, Wong N, Leip E, Kannel W, Levy W. Does the relation of blood pressure to coronary heart disease risk change with aging? Circulation. 2001;103:1245–1249. - PubMed
-
- Belsley DA, Kuh E, Welsch RE. Regression Diagnostics. New York, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1980.
-
- Xu J, Bleecker E, Jongepier H, Howard T, Koppelman G, Postma D, Meyers D. Major recessive gene(s) with considerable residual polygenic effect regulating adult height: confirmation of genome-wide scan results for chromosomes 6, 9, and 12. Am J Hum Genet. 2002;71:646–650. doi: 10.1086/342216. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical