Bacterial volatiles induce systemic resistance in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 14976231
- PMCID: PMC389924
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.026583
Bacterial volatiles induce systemic resistance in Arabidopsis
Erratum in
- Plant Physiol. 2005 Apr;137(4):1486
Abstract
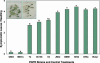
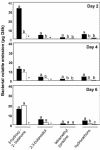
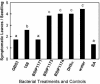
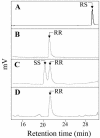
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, in association with plant roots, can trigger induced systemic resistance (ISR). Considering that low-molecular weight volatile hormone analogues such as methyl jasmonate and methyl salicylate can trigger defense responses in plants, we examined whether volatile organic compounds (VOCs) associated with rhizobacteria can initiate ISR. In Arabidopsis seedlings exposed to bacterial volatile blends from Bacillus subtilis GB03 and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens IN937a, disease severity by the bacterial pathogen Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora was significantly reduced compared with seedlings not exposed to bacterial volatiles before pathogen inoculation. Exposure to VOCs from rhizobacteria for as little as 4 d was sufficient to activate ISR in Arabidopsis seedlings. Chemical analysis of the bacterial volatile emissions revealed the release of a series of low-molecular weight hydrocarbons including the growth promoting VOC (2R,3R)-(-)-butanediol. Exogenous application of racemic mixture of (RR) and (SS) isomers of 2,3-butanediol was found to trigger ISR and transgenic lines of B. subtilis that emitted reduced levels of 2,3-butanediol and acetoin conferred reduced Arabidopsis protection to pathogen infection compared with seedlings exposed to VOCs from wild-type bacterial lines. Using transgenic and mutant lines of Arabidopsis, we provide evidence that the signaling pathway activated by volatiles from GB03 is dependent on ethylene, albeit independent of the salicylic acid or jasmonic acid signaling pathways. This study provides new insight into the role of bacteria VOCs as initiators of defense responses in plants.
Figures



References
-
- Alonso JM, Hirayama T, Roman G, Nourizadeh S, Ecker JR (1999) Ein2 a bifunctional transducer of ethylene and stress responses in Arabidopsis. Science 284: 2148-2152 - PubMed
-
- Alström S (1991) Induction of disease resistance in common bean susceptible to halo blight bacterial pathogen after seed bacterization with rhizosphere pseudomonads. J Gen Appl Microbiol 37: 495-501
-
- Arimura G, Ozawa R, Horiuchi JI, Nishioka T, Takabayashi J (2001) Plant-plant interactions mediated by volatiles emitted from plants infested by spider mites. Biochem System Ecol 29: 1049-1061
-
- Arimura G, Ozawa R, Shimoda T, Nishioka T, Boland W, Takabayashi J (2000) Herbivory-induced volatiles elicit defense genes in lima bean leaves. Nature 406: 512-515 - PubMed
-
- Benhamou N, Kloepper JW, Tuzun S (1998) Induction of resistance against Fusarium wilt of tomato by combination of chitosan with an endophytic bacterial strain: ultrastructure and cytochemistry of the host response. Planta 204: 153-168
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

