Disruption of TRPM6/TRPM7 complex formation by a mutation in the TRPM6 gene causes hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia
- PMID: 14976260
- PMCID: PMC365716
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0305252101
Disruption of TRPM6/TRPM7 complex formation by a mutation in the TRPM6 gene causes hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia
Abstract
Impaired magnesium reabsorption in patients with TRPM6 gene mutations stresses an important role of TRPM6 (melastatin-related TRP cation channel) in epithelial magnesium transport. While attempting to isolate full-length TRPM6, we found that the human TRPM6 gene encodes multiple mRNA isoforms. Full-length TRPM6 variants failed to form functional channel complexes because they were retained intracellularly on heterologous expression in HEK 293 cells and Xenopus oocytes. However, TRPM6 specifically interacted with its closest homolog, the Mg(2+)-permeable cation channel TRPM7, resulting in the assembly of functional TRPM6/TRPM7 complexes at the cell surface. The naturally occurring S141L TRPM6 missense mutation abrogated the oligomeric assembly of TRPM6, thus providing a cell biological explanation for the human disease. Together, our data suggest an important contribution of TRPM6/TRPM7 heterooligomerization for the biological role of TRPM6 in epithelial magnesium absorption.
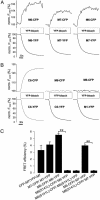
Figures
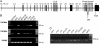
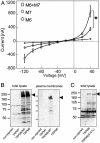
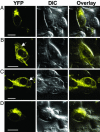
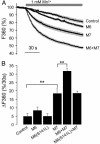
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

